オンラインで CPU 使用率が最も高い Perl コードパスを素早く特定する方法(OpenResty XRay を使用)
本日は、OpenResty XRay を使用して、実行中の Perl プロセスにおいて CPU 時間を最も消費している Perl コードパスを素早く特定する方法を段階的にご紹介します。これらのコードパスは CPU 時間を最も消費し、アプリケーションのパフォーマンスに影響を与えます。
問題: 高 CPU 使用率
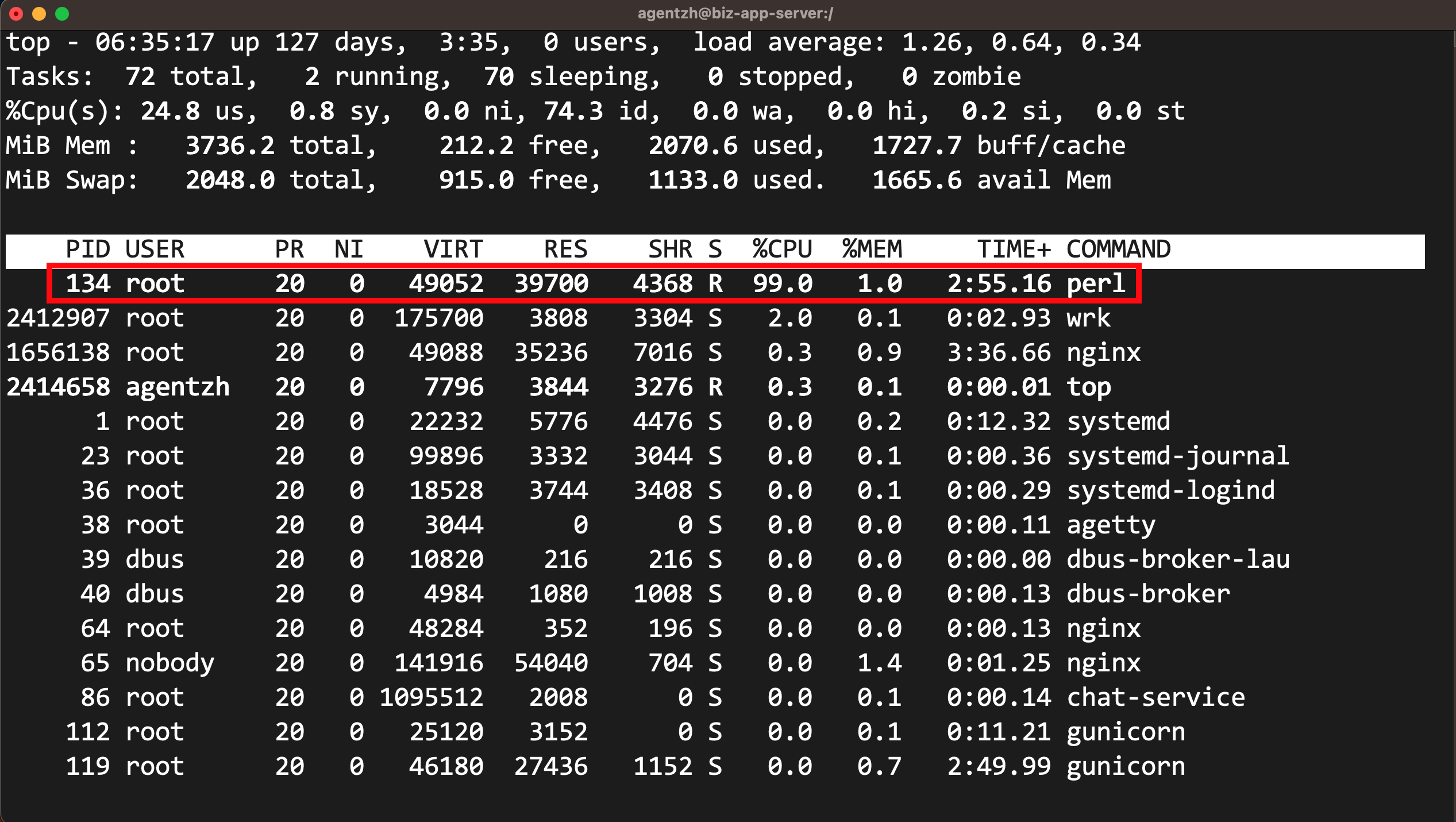
まず、top コマンドを実行して CPU 使用状況を確認します。
ご覧のように、1 つの Perl プロセスが CPU コアリソースの 100% を占有しています。
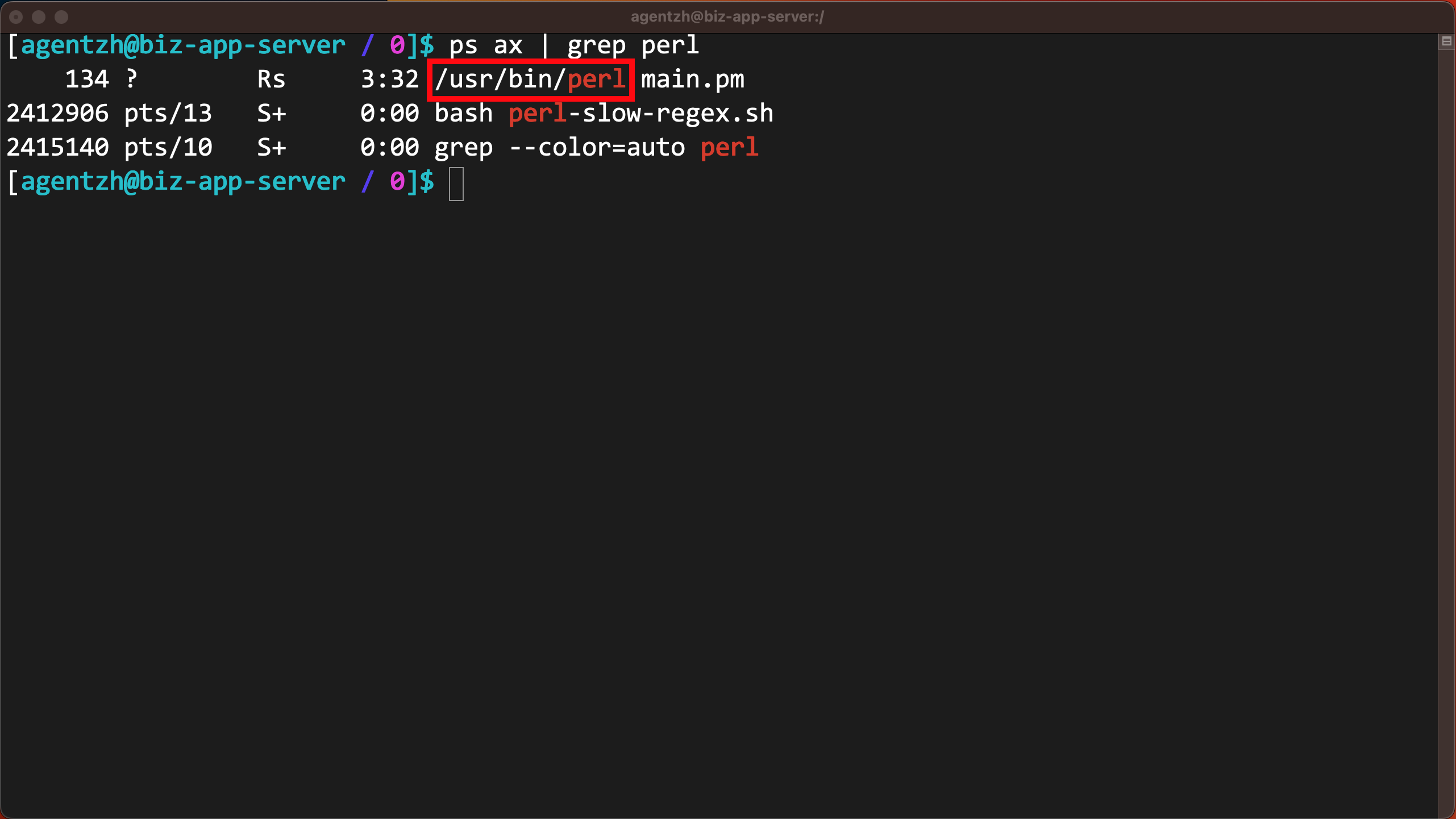
ps コマンドを実行して、このプロセスの完全なコマンドラインを確認します。
これが Linux ディストリビューションに付属の標準 Perl バイナリ実行ファイルであることがわかります。
最も CPU 使用率の高い Perl コードパスを特定
OpenResty XRayを使用して、この未修正のプロセスを検査してみましょう。リアルタイムで分析を行い、CPU 使用率が高い理由を明らかにします。
ブラウザで OpenResty XRayの Web コンソールを開きます。
現在分析中のマシンが正しいことを確認してください。
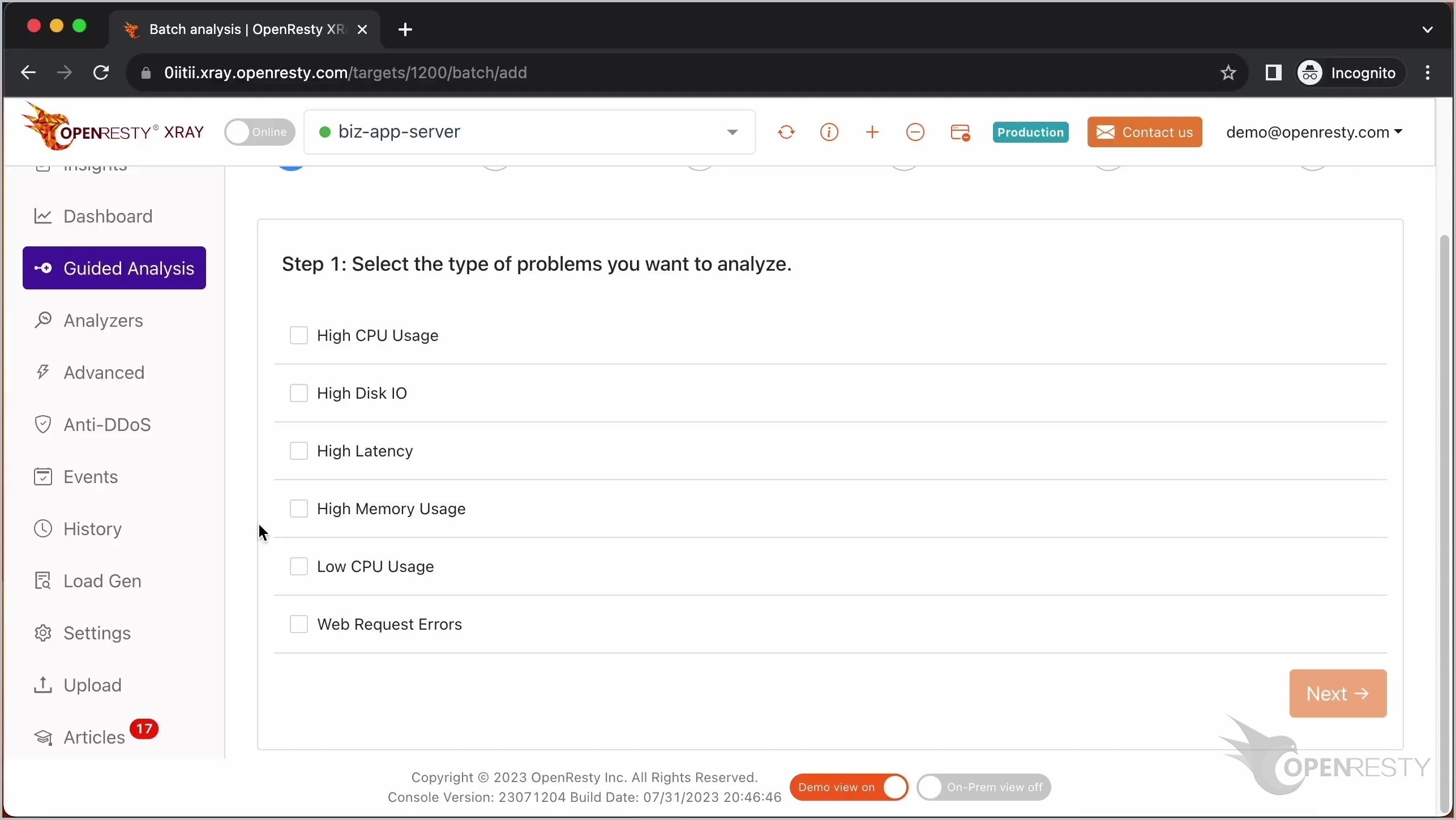
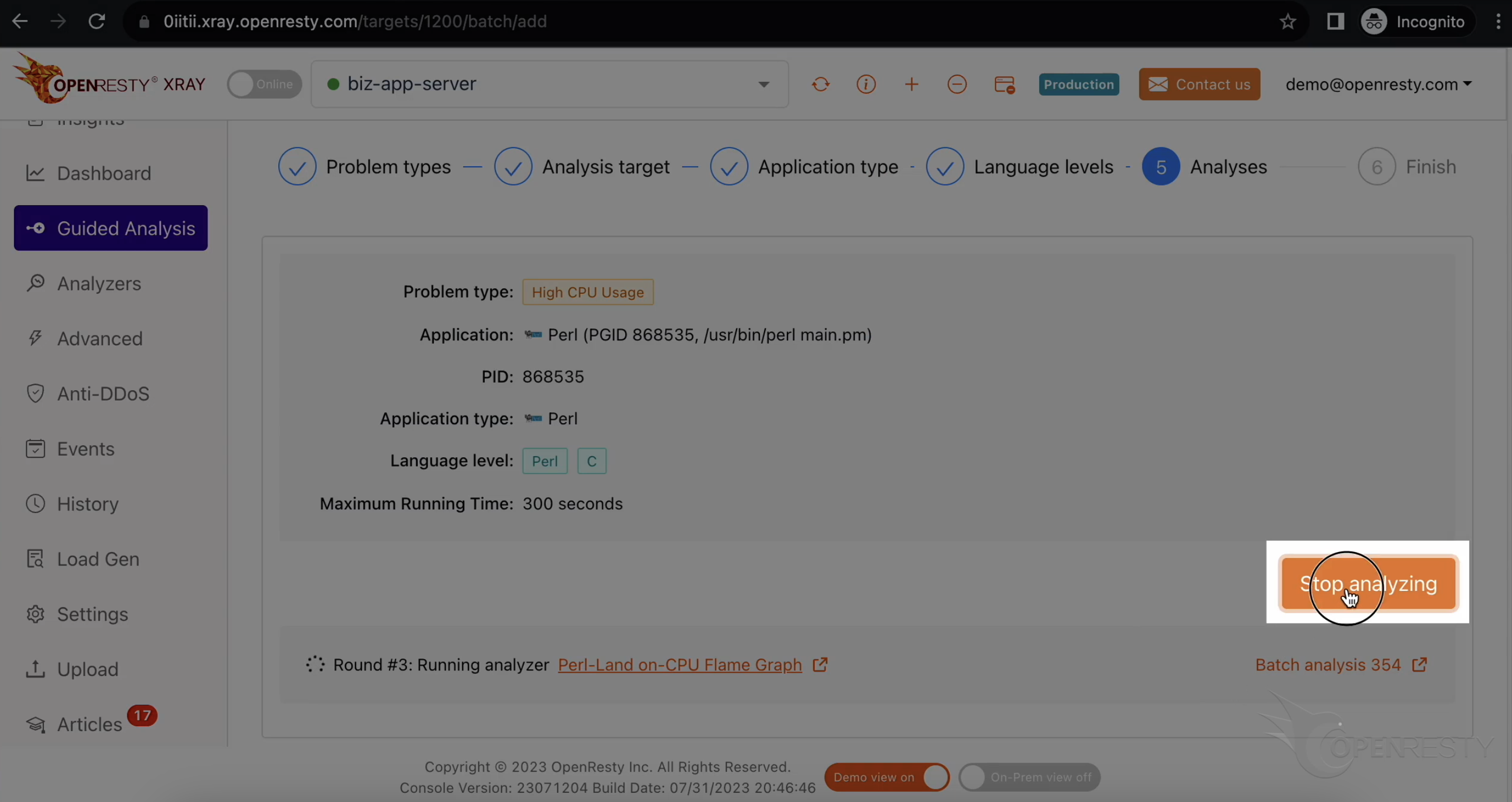
「Guided Analysis」ページに移動します。
ここでは、システムが分析可能な各種の問題を確認できます。
「High CPU Usage」を選択します。
「Next」をクリックします。
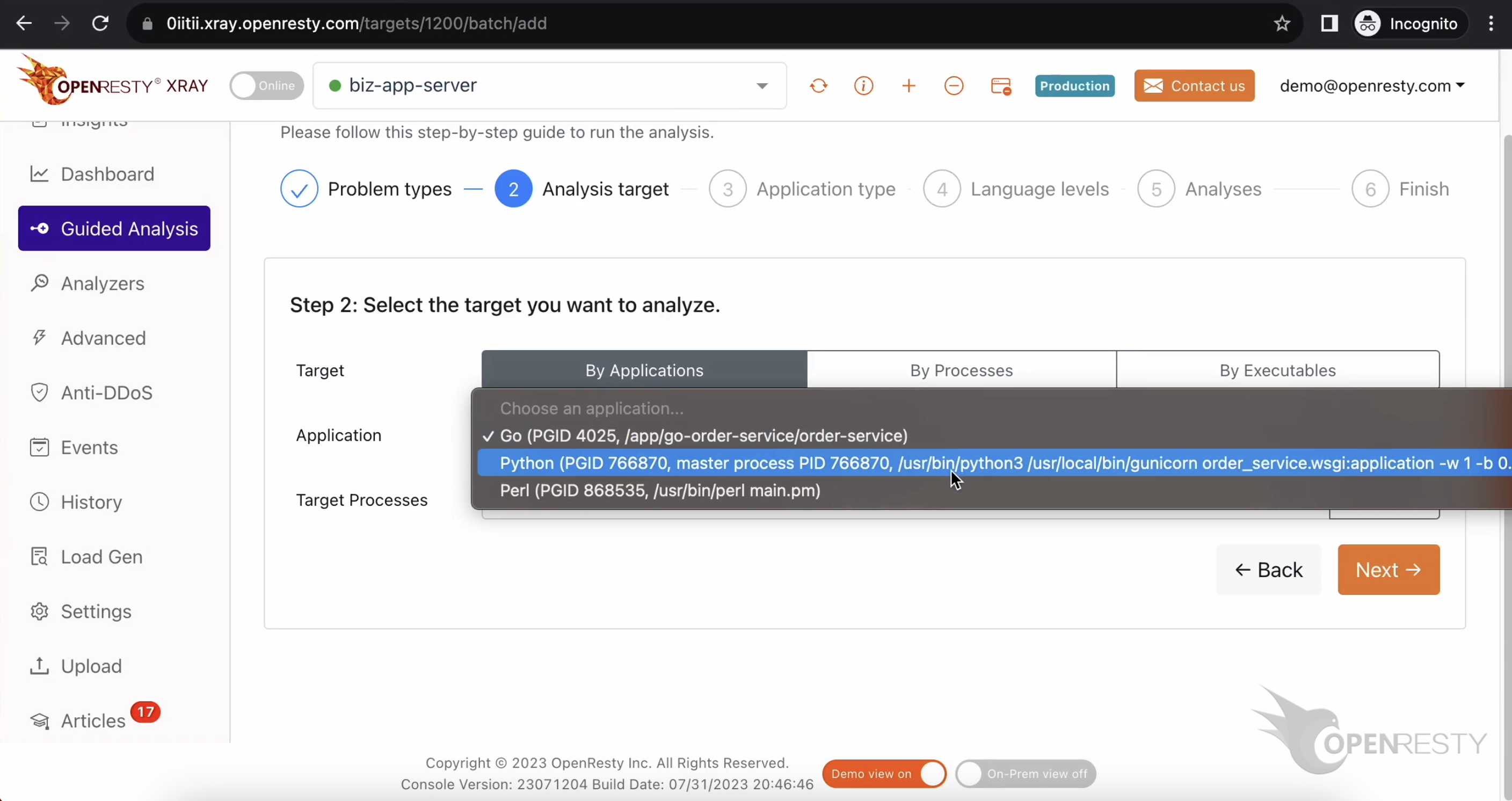
Perl アプリケーションを選択します。
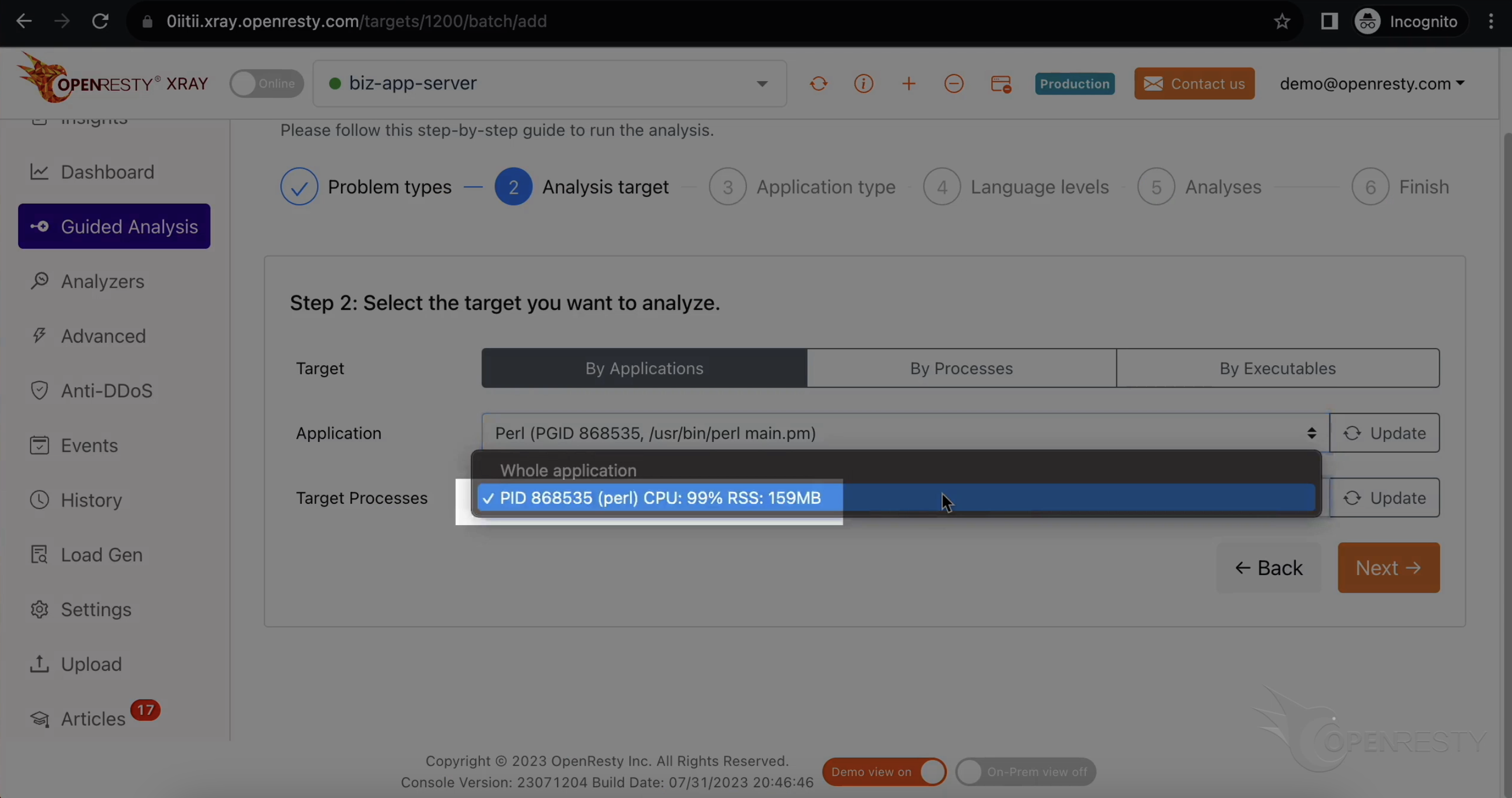
CPU リソースの 99% を消費しているプロセスを選択します。これは先ほど top で確認したプロセスです。
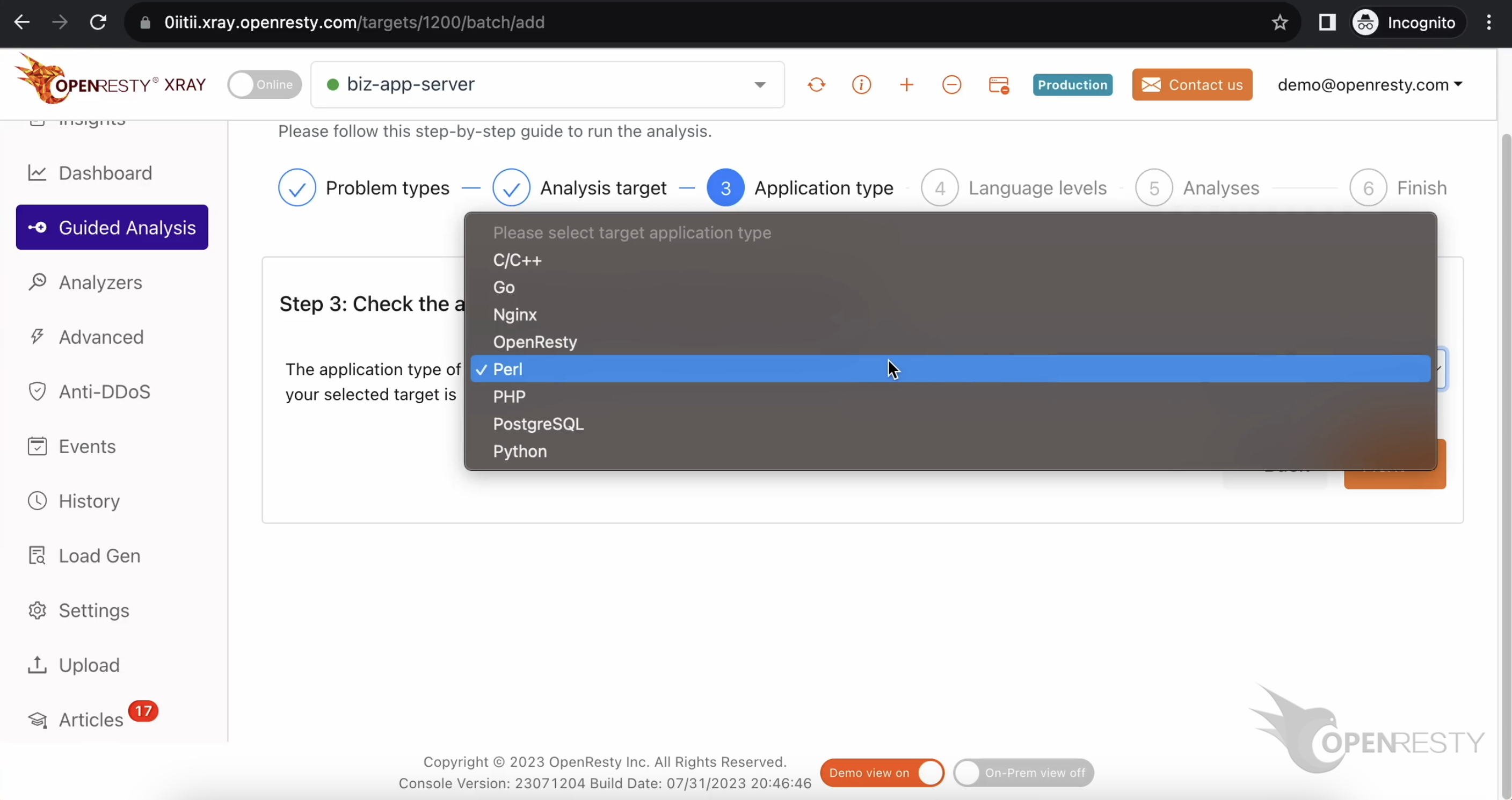
アプリケーションのタイプが正しいことを確認します。通常、デフォルト値が正しいです。
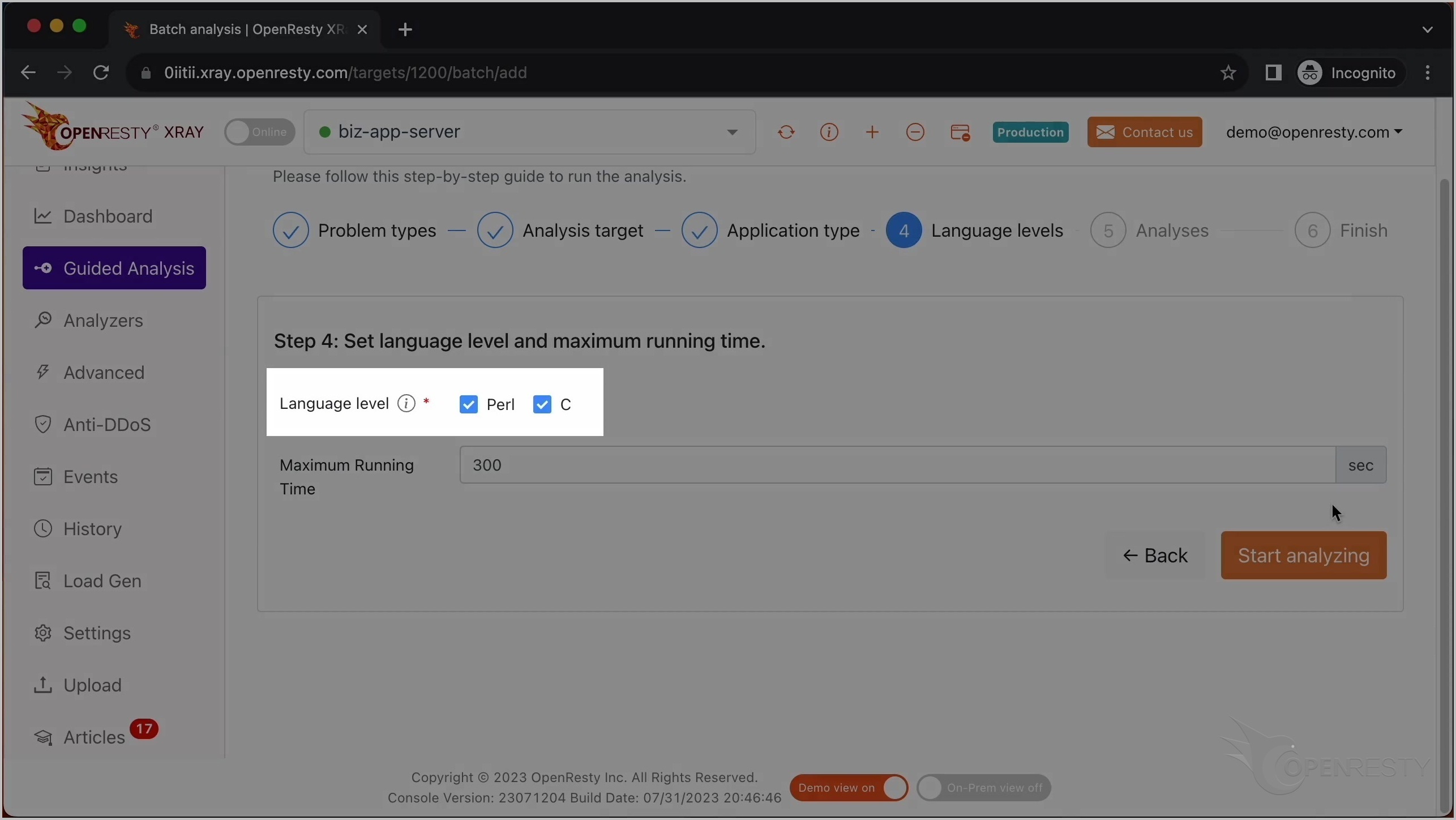
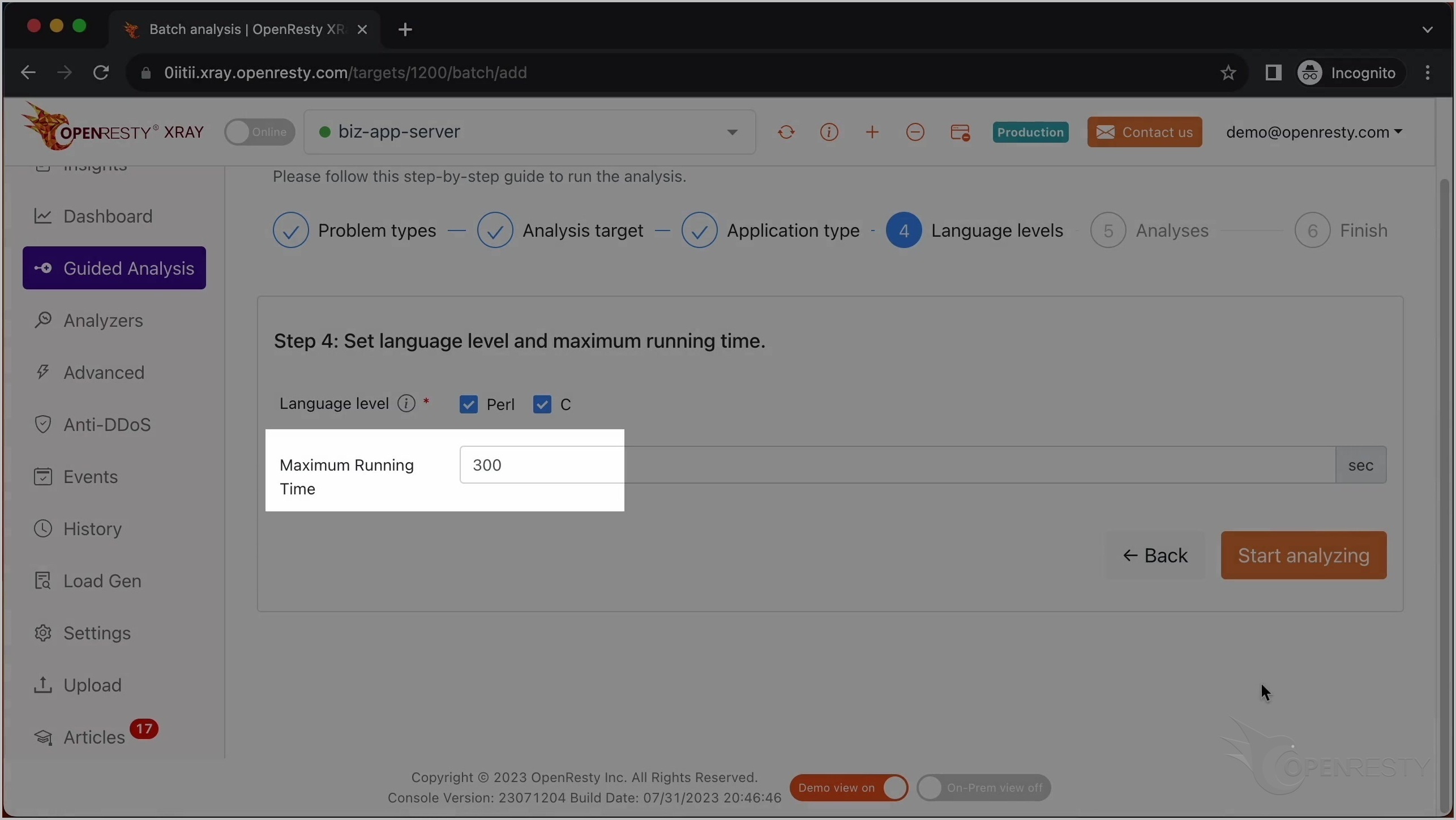
OpenResty XRay は、様々な言語レベルで分析を行うことができます。ここでは Perl と C の両方を選択したままにします。
最長分析時間を設定することもできます。ここではデフォルトの 300 秒のままにします。
分析を開始します。
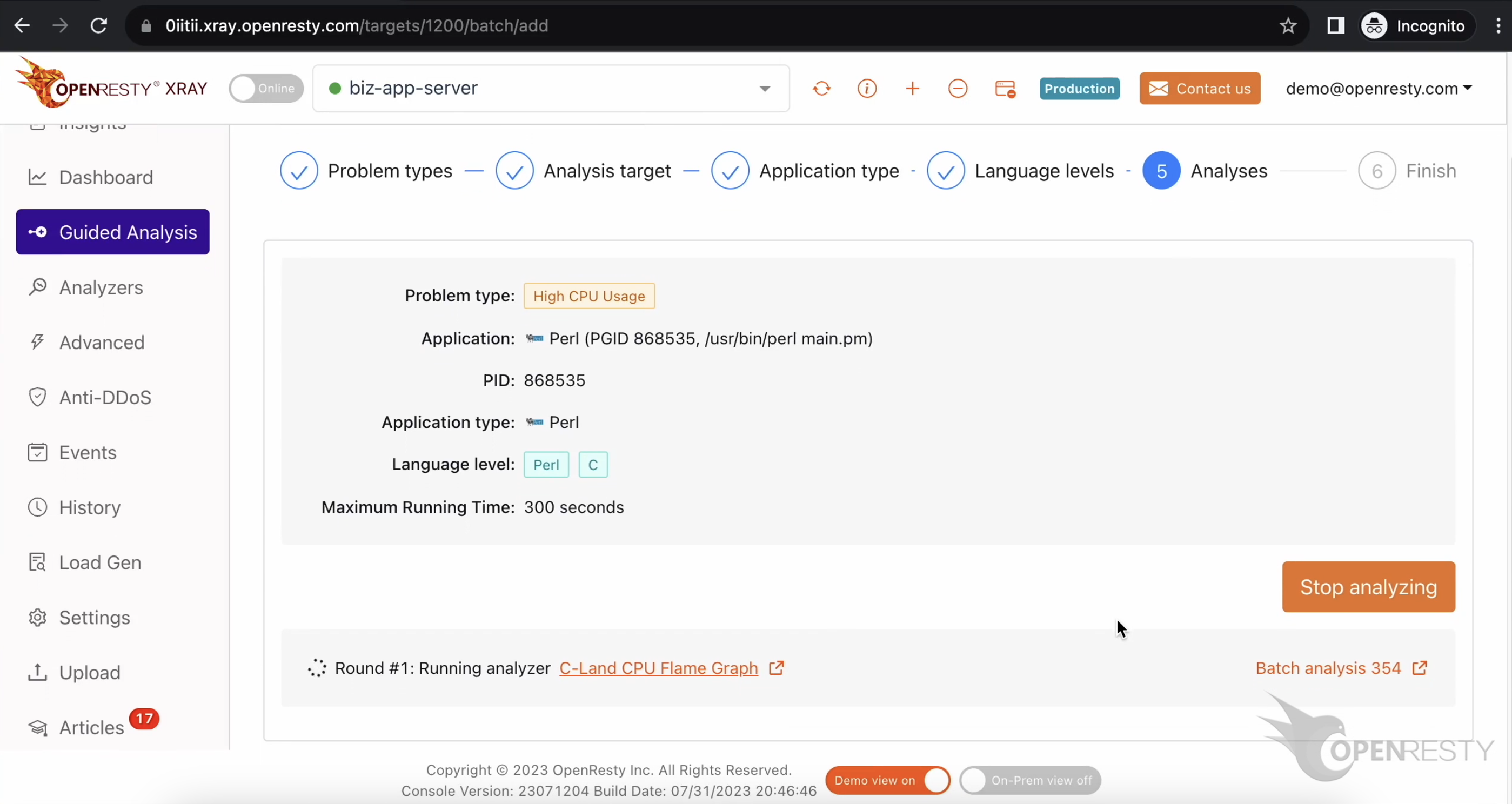
システムは複数回の分析を継続的に実行します。現在、初回の分析を実行中です。
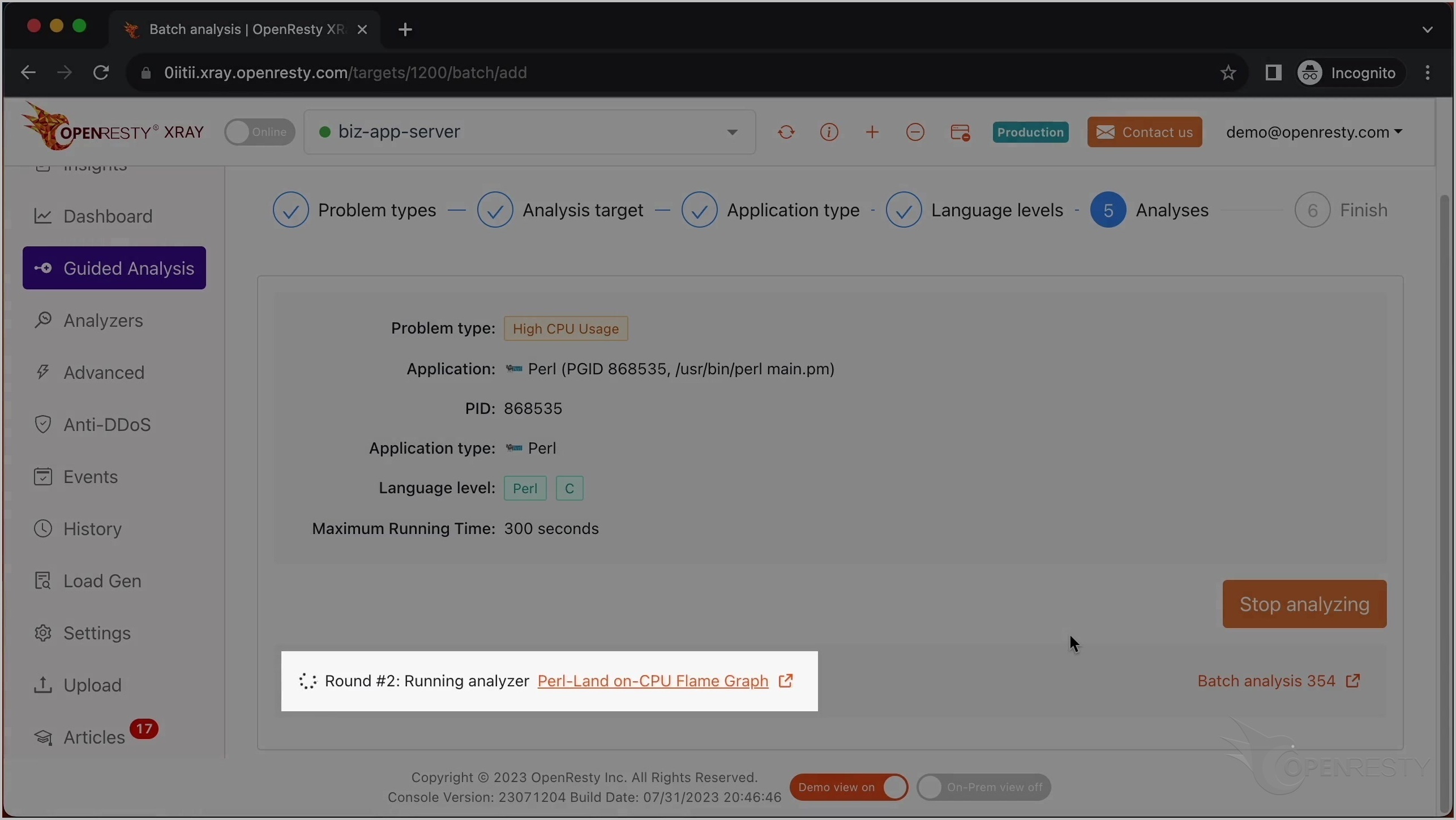
初回の分析が完了し、現在 2 回目のラウンドに入っています。この例では、1 回の分析で十分です。
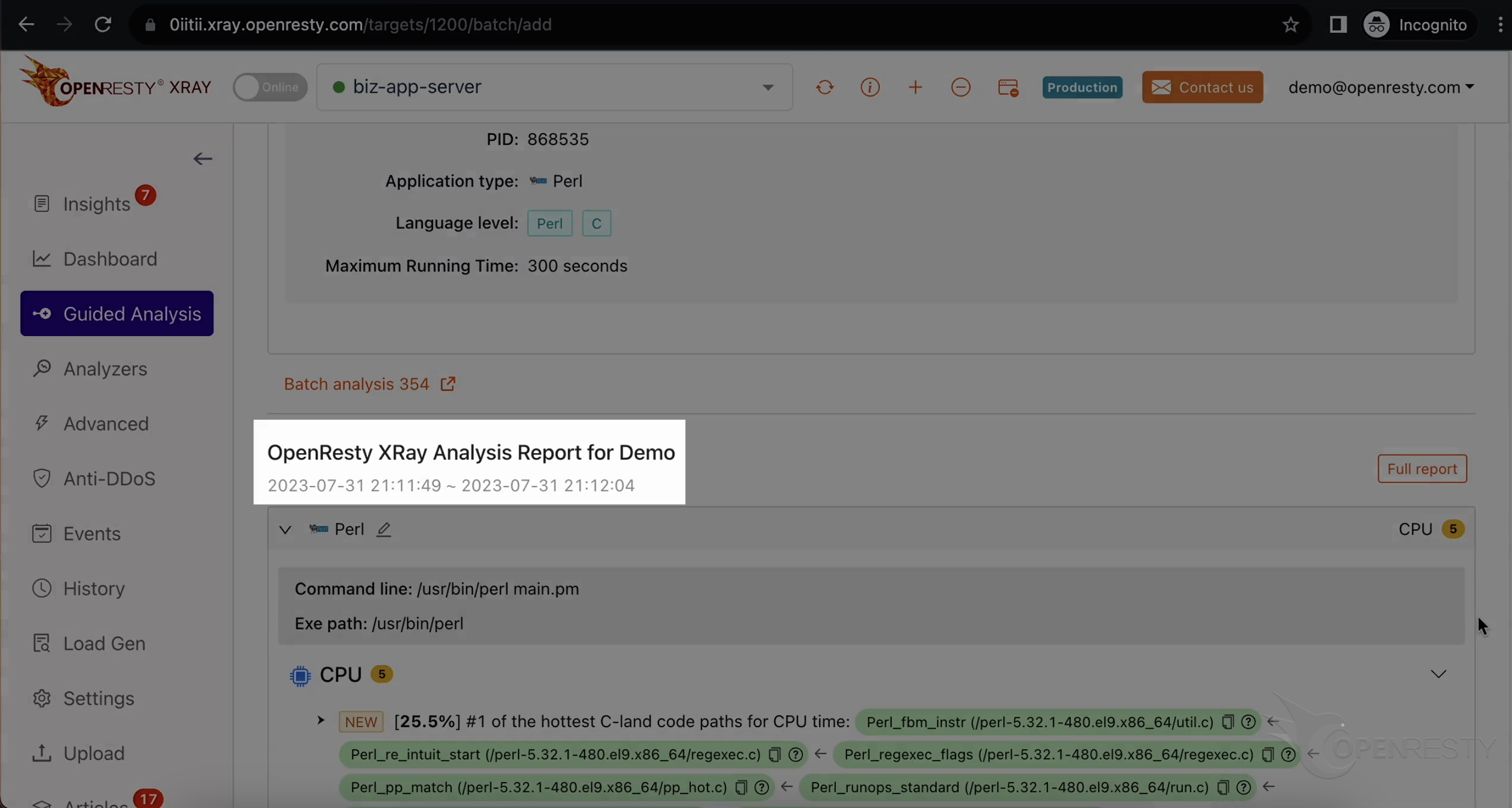
分析を停止します。
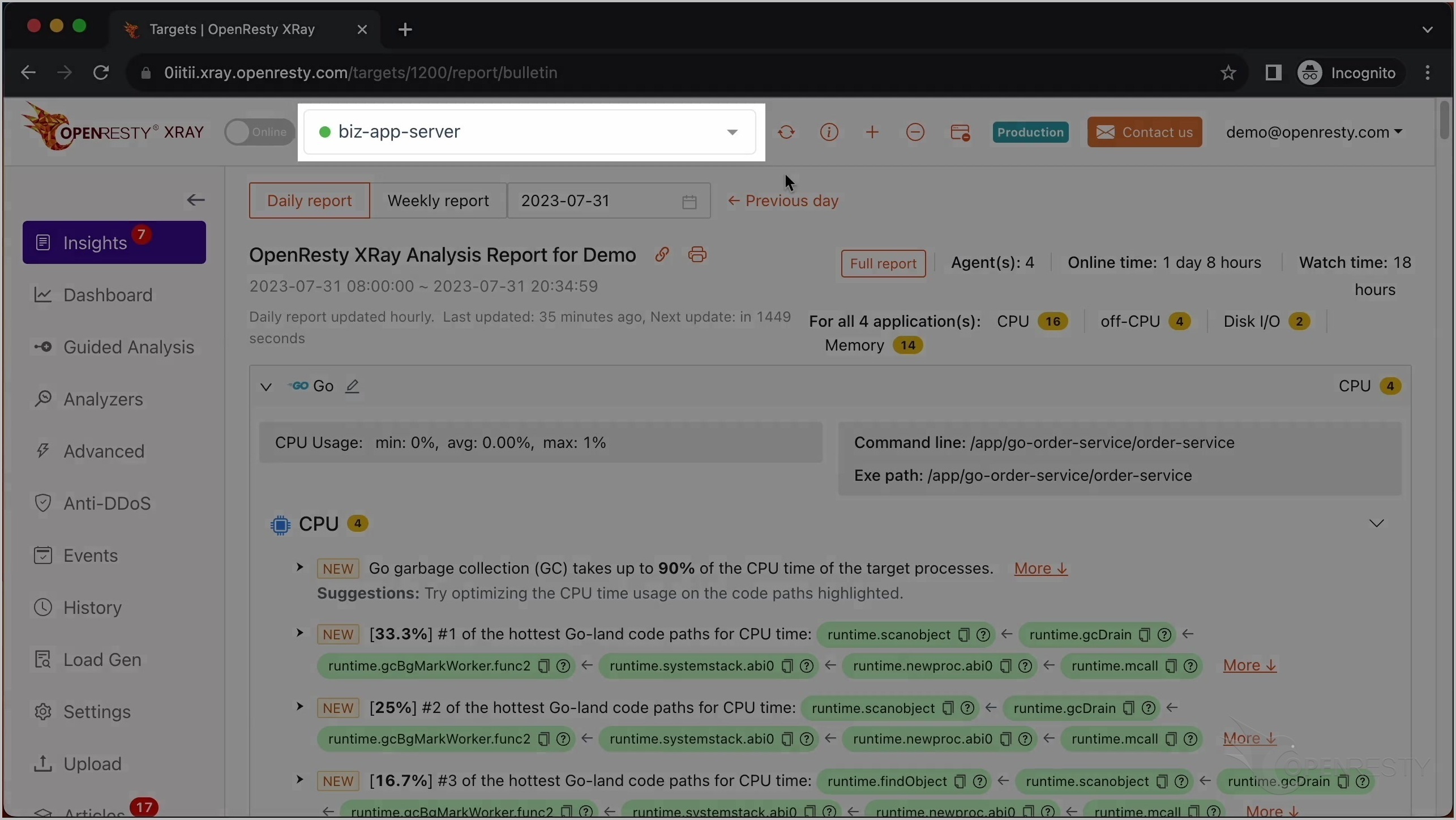
自動生成された分析レポートが表示されます。
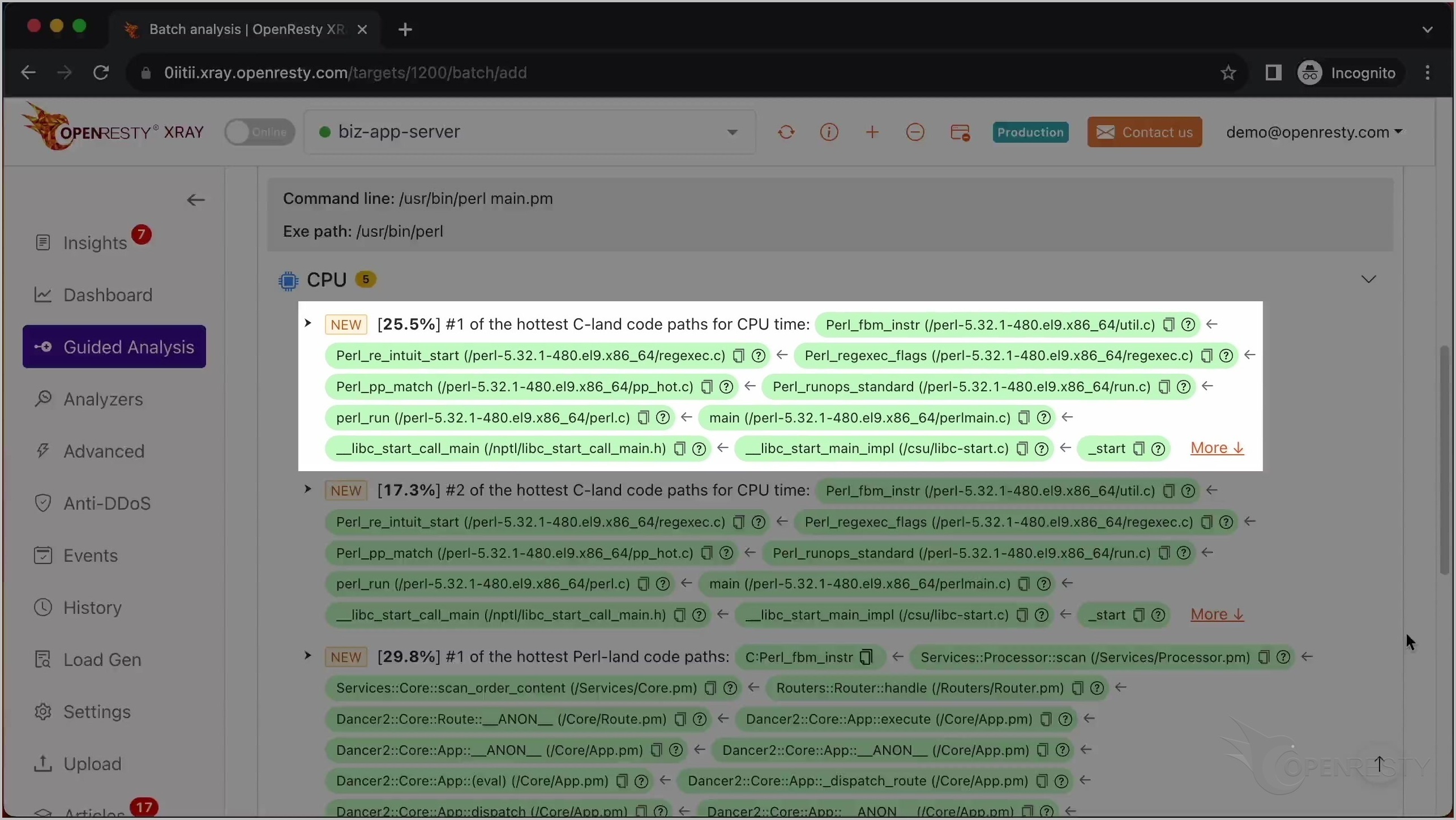
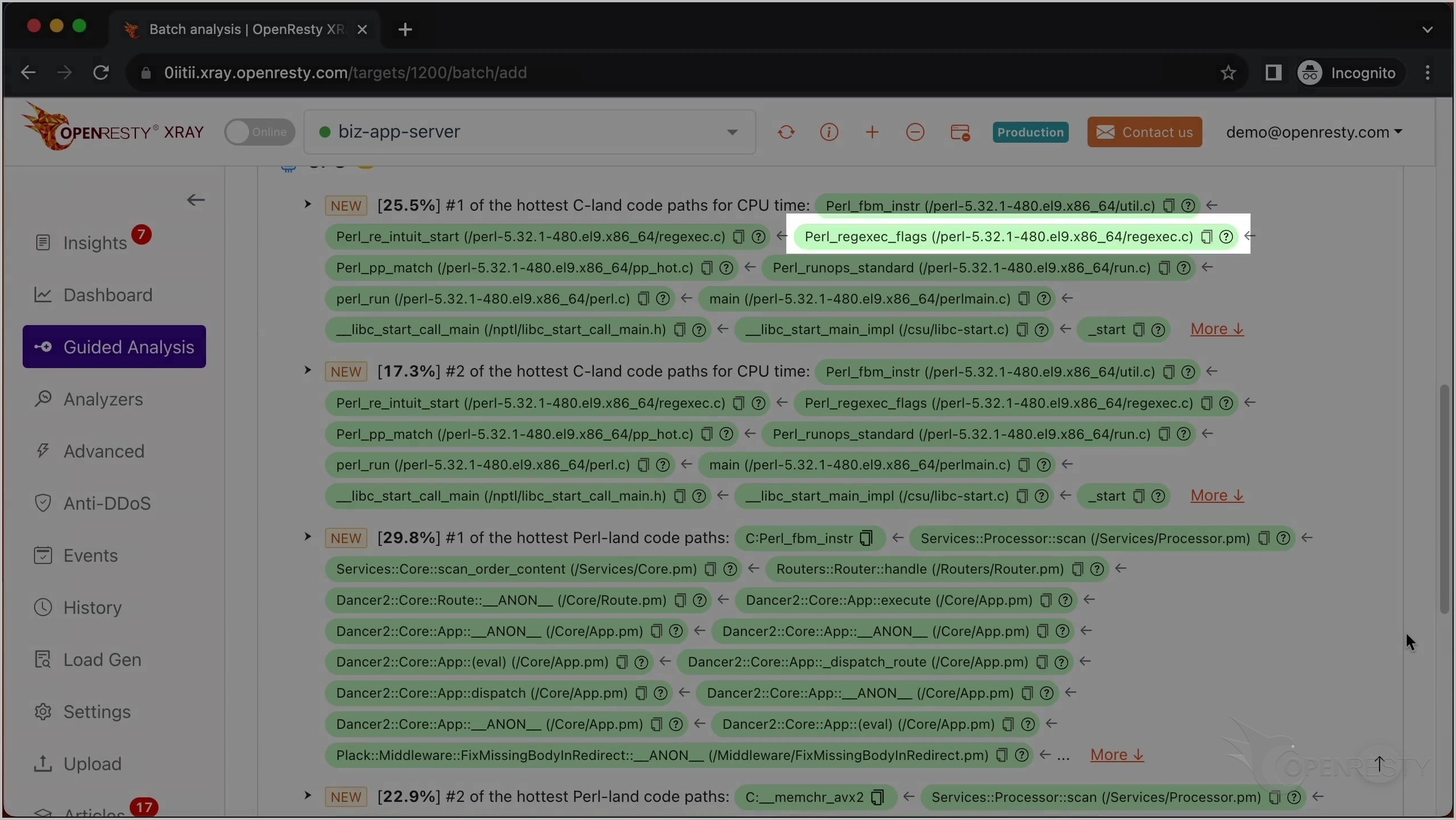
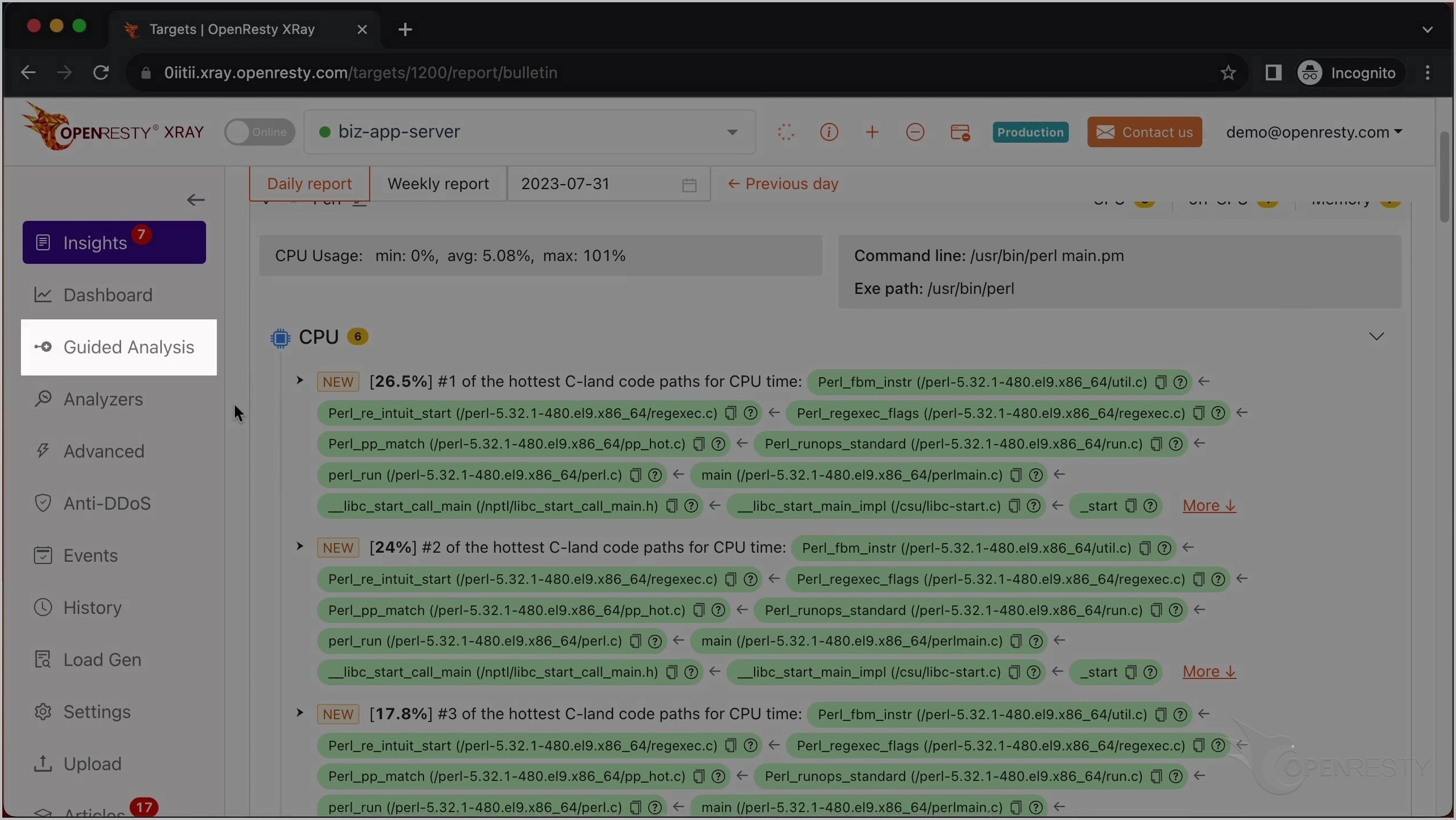
これが CPU 使用率が最も高い C コードパスです。
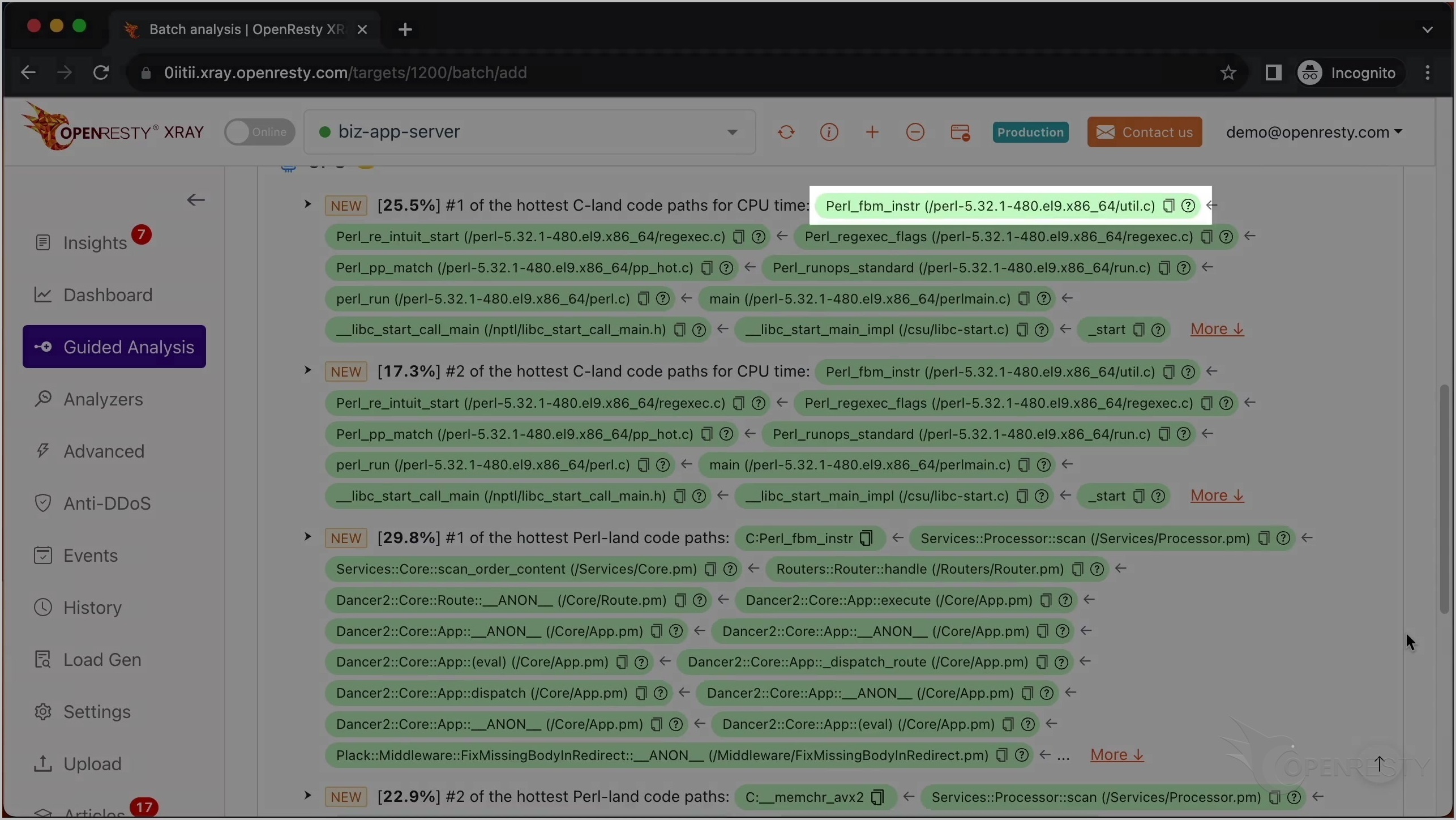
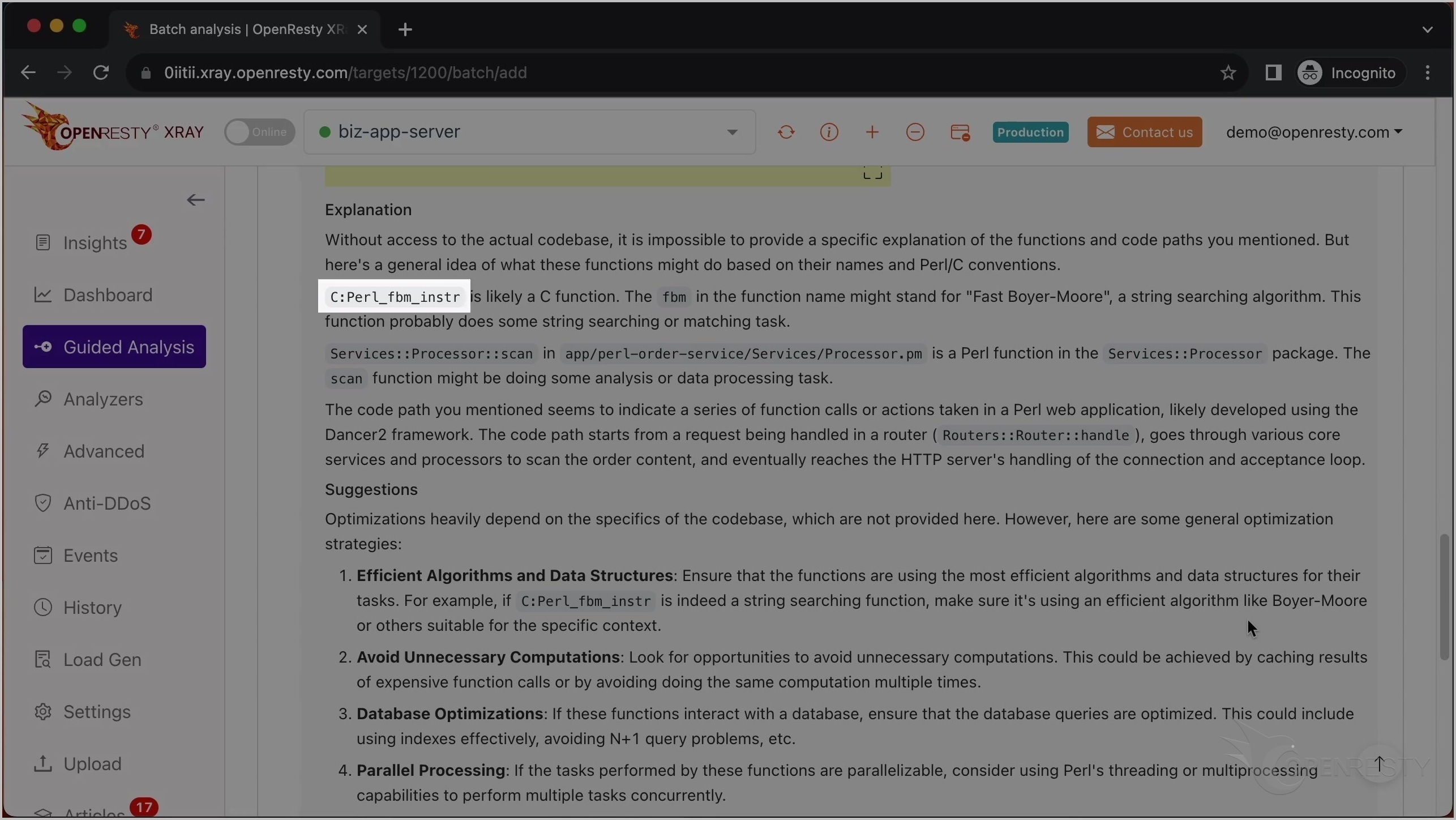
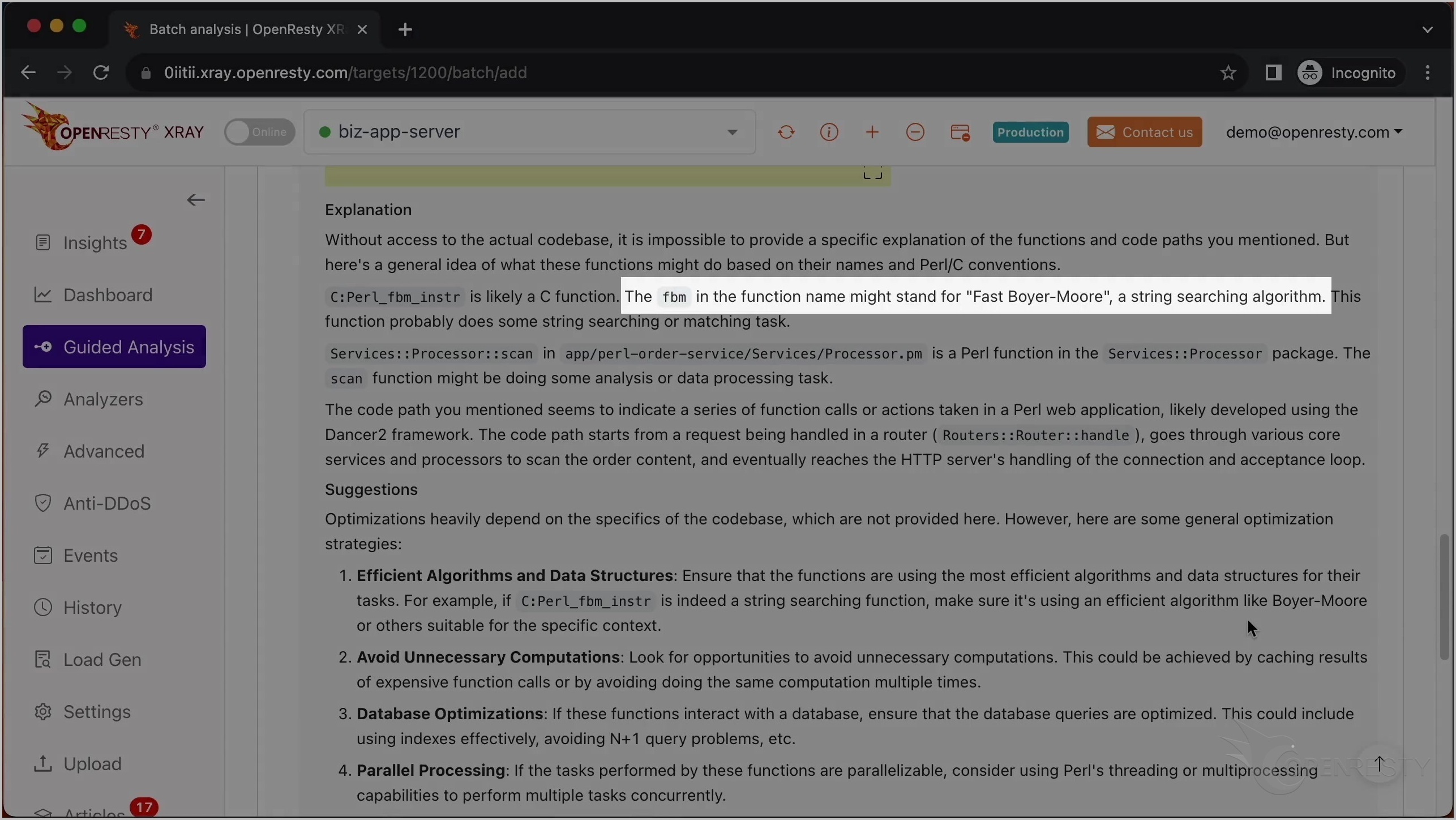
これは Perl VM ランタイム内の Perl_fbm_instr という C 関数です。正規表現マッチングのために FBM アルゴリズムを使用して文字列を検索しています。
ここの C 関数は、確かに正規表現マッチングを行っていることを示しています。
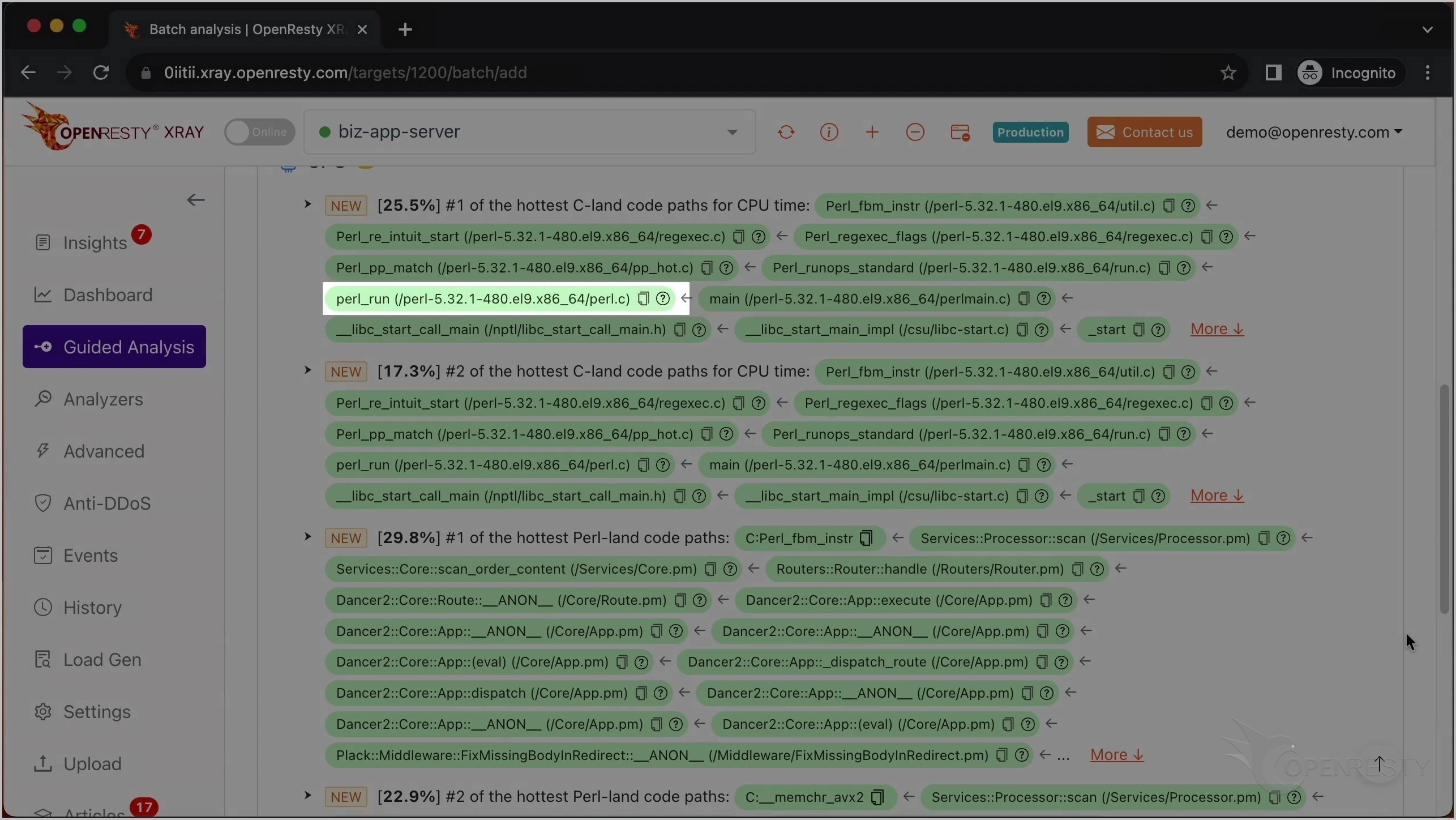
perl_run 関数は、Perl VM が現在 Perl コードを実行していることを意味します。
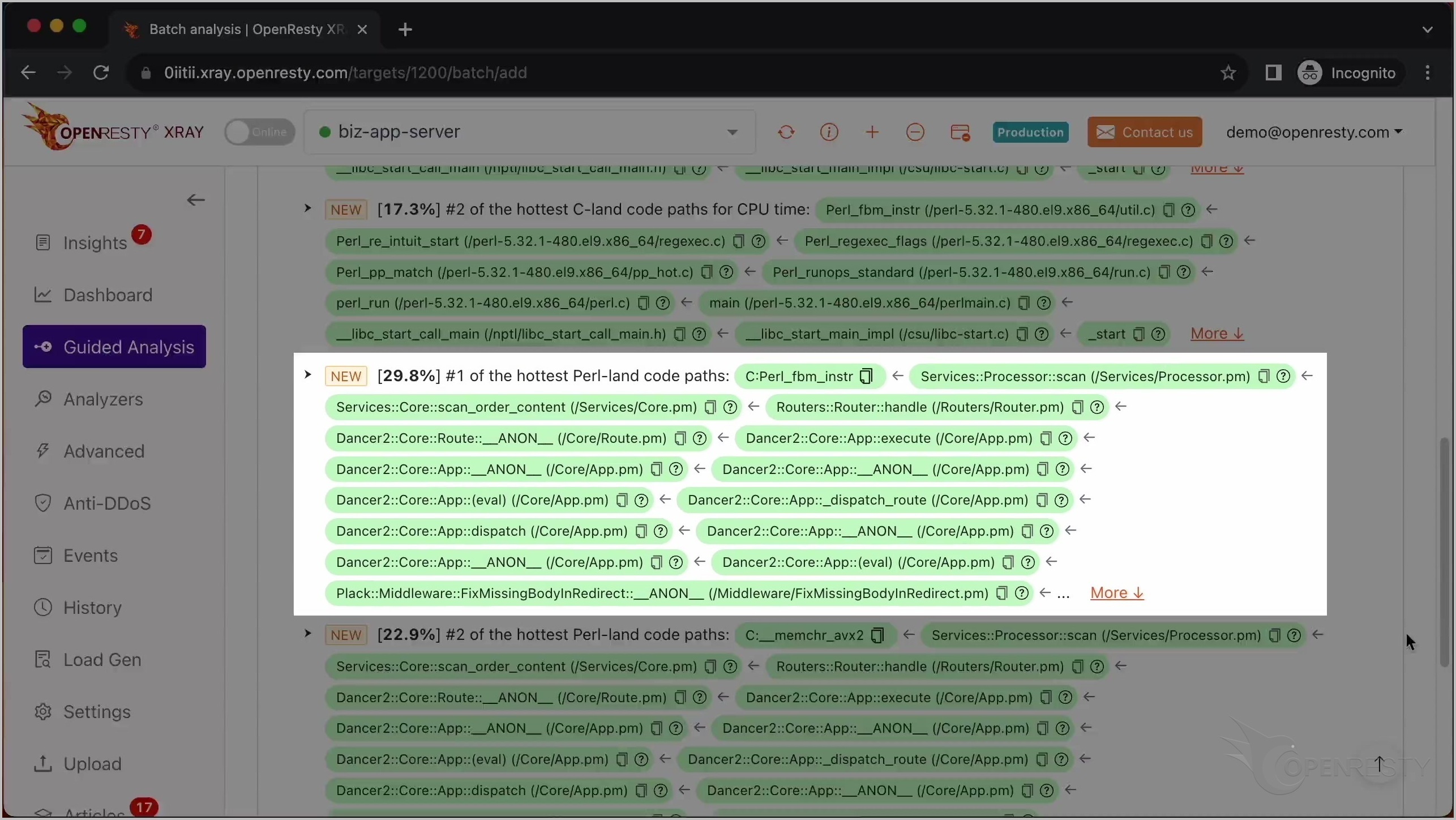
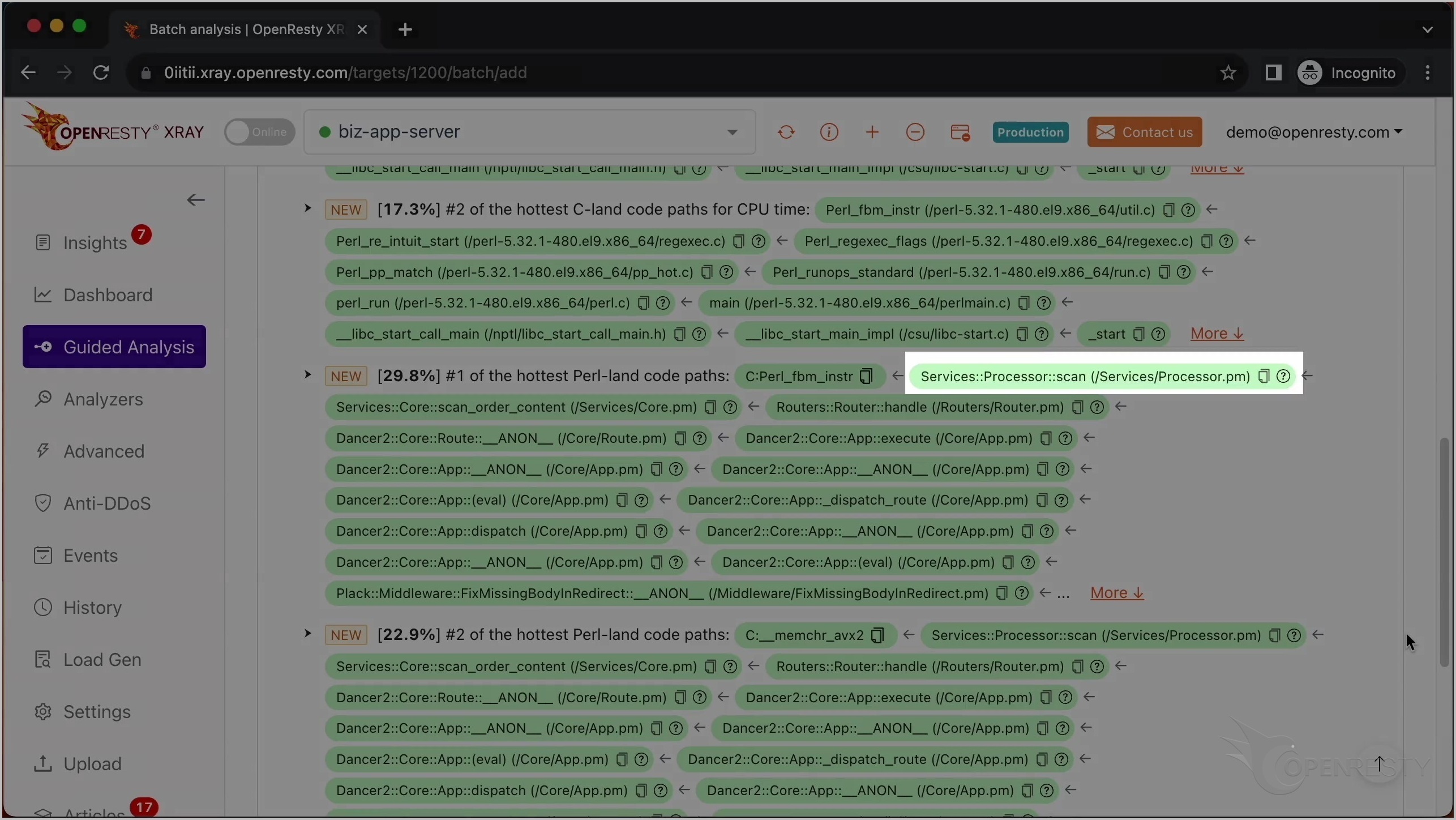
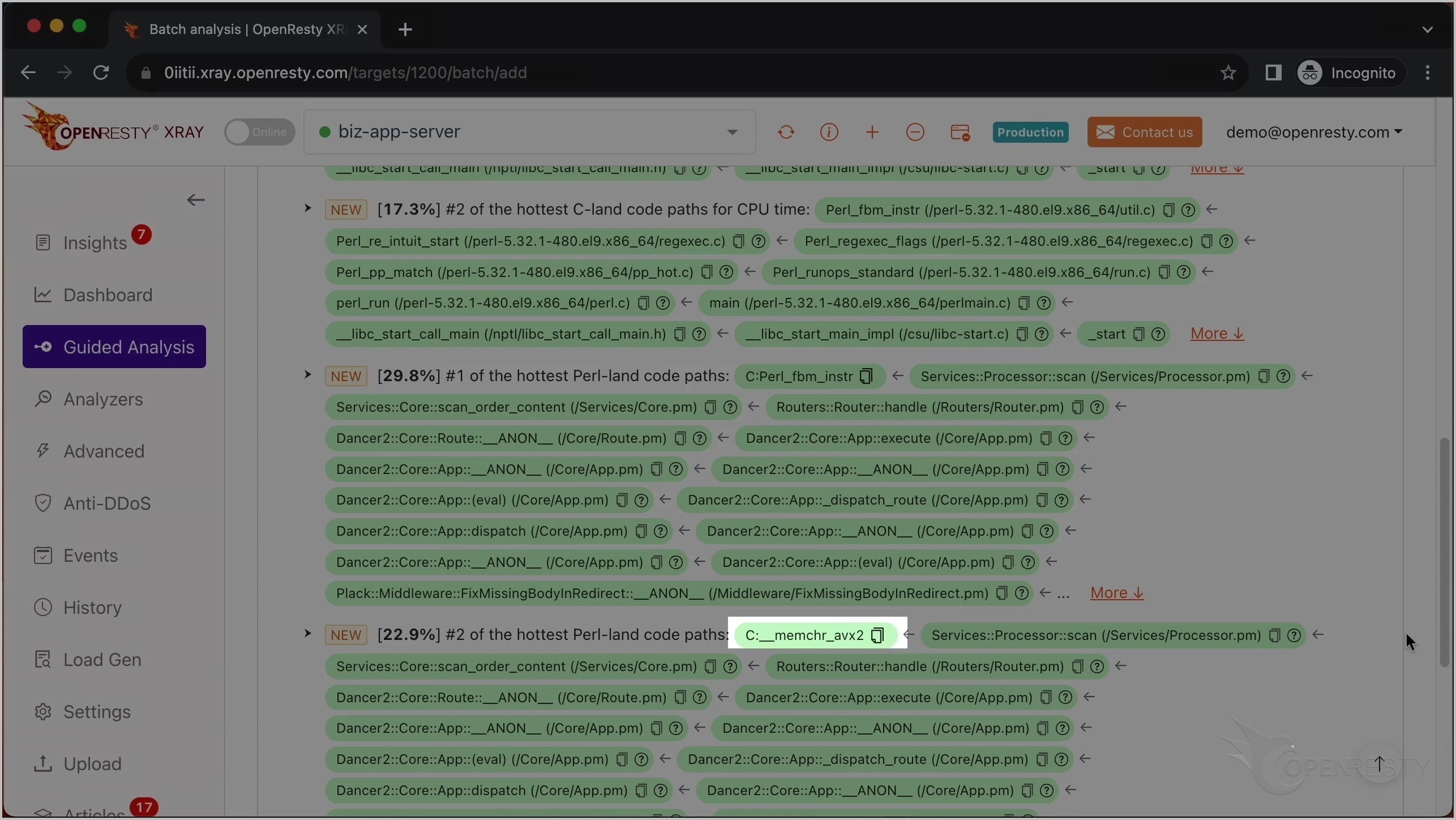
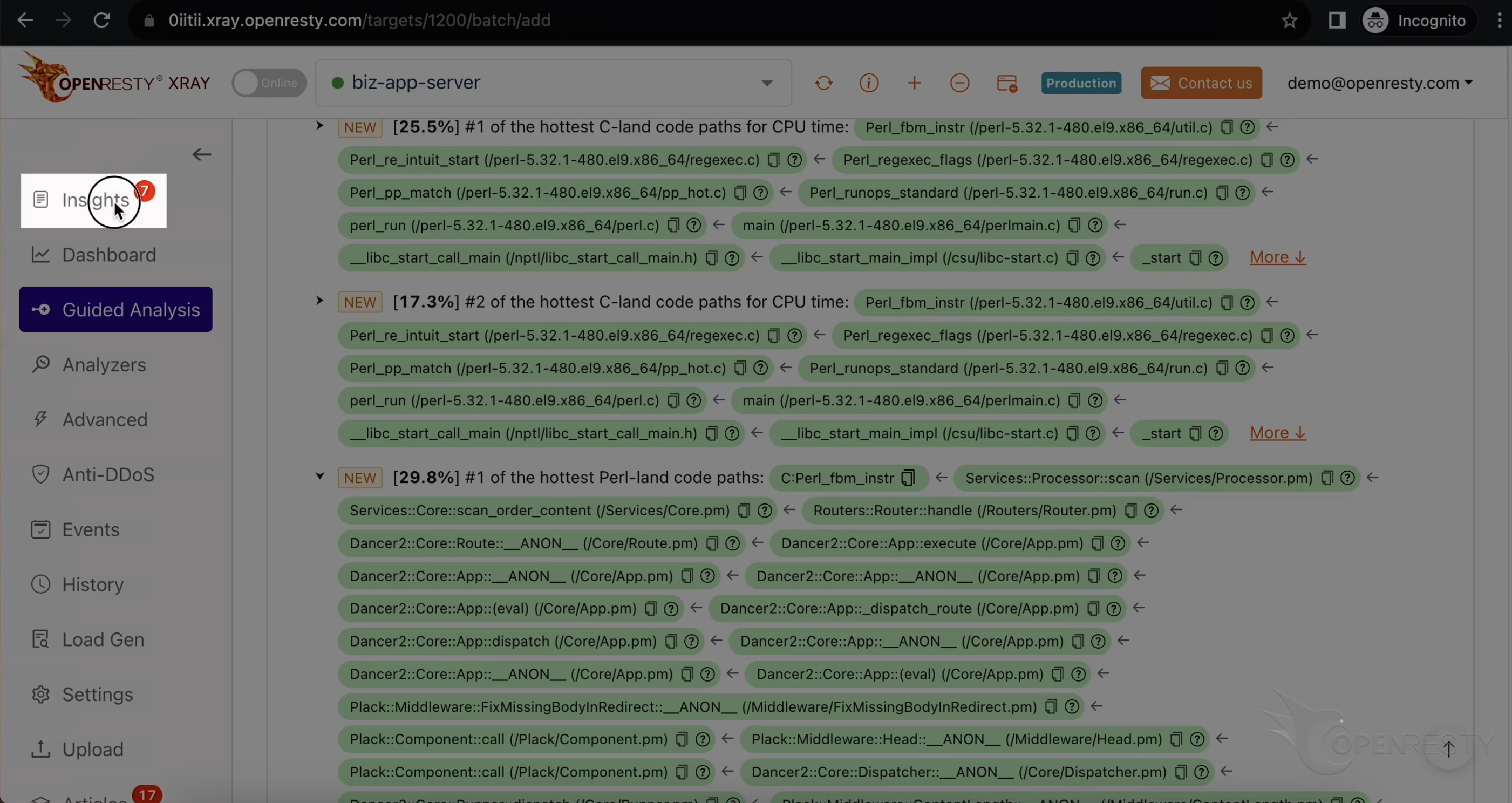
最も CPU 使用率の高い C コードパスを確認した後、最も CPU 使用率の高い Perl コードパスを見てみましょう。
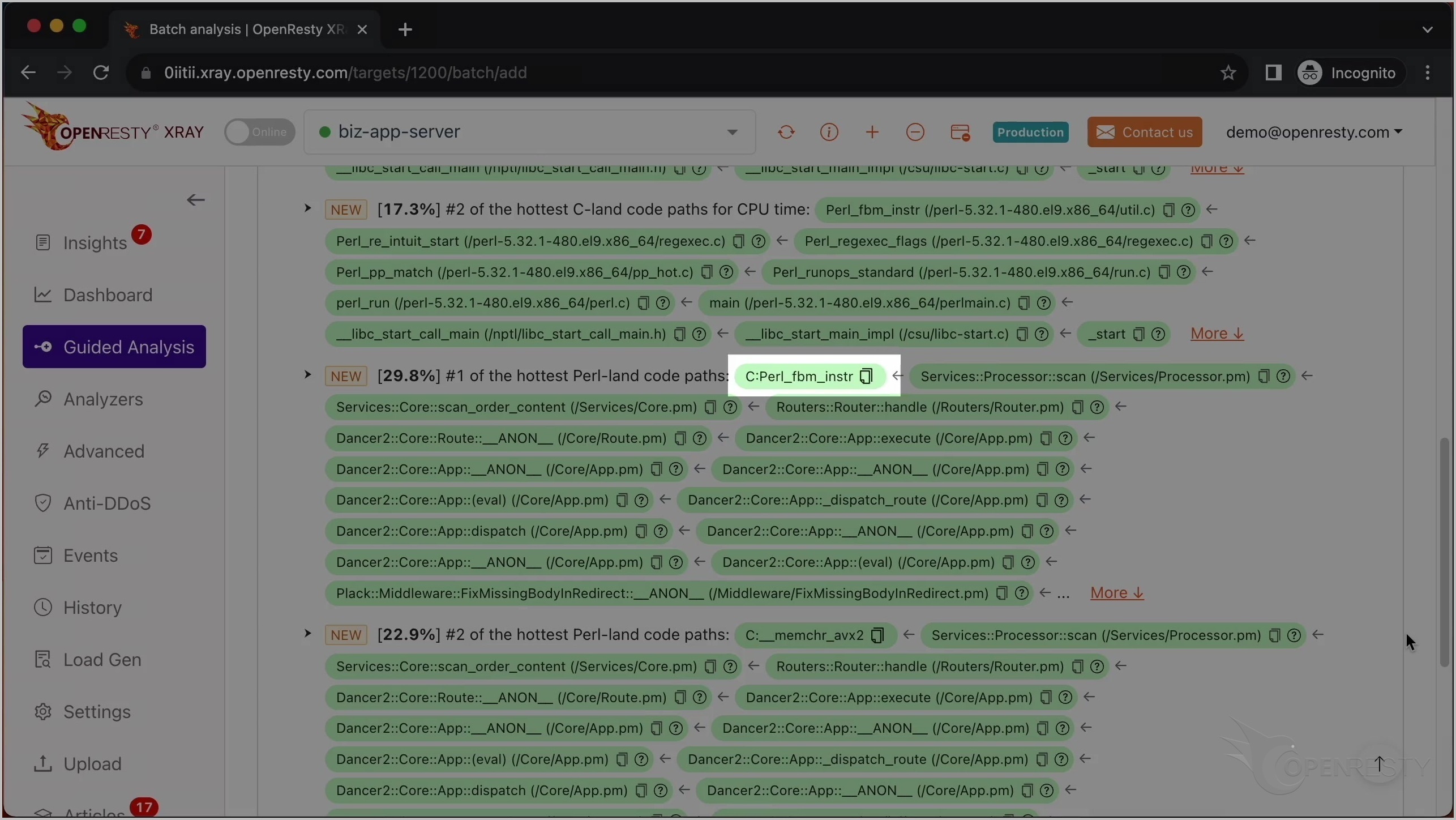
この C 関数は、先ほど説明した Perl_fbm_instr と同じです。
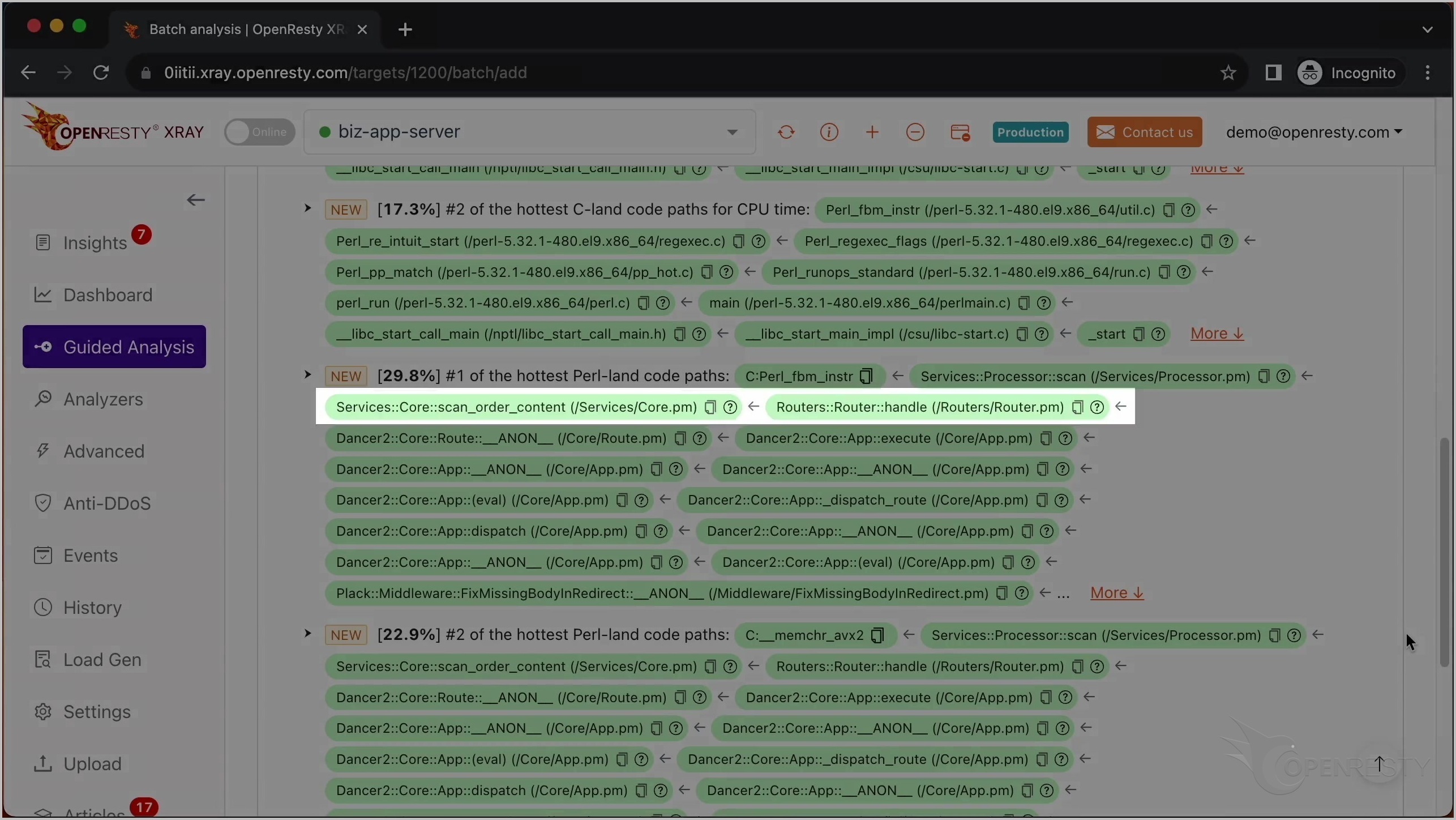
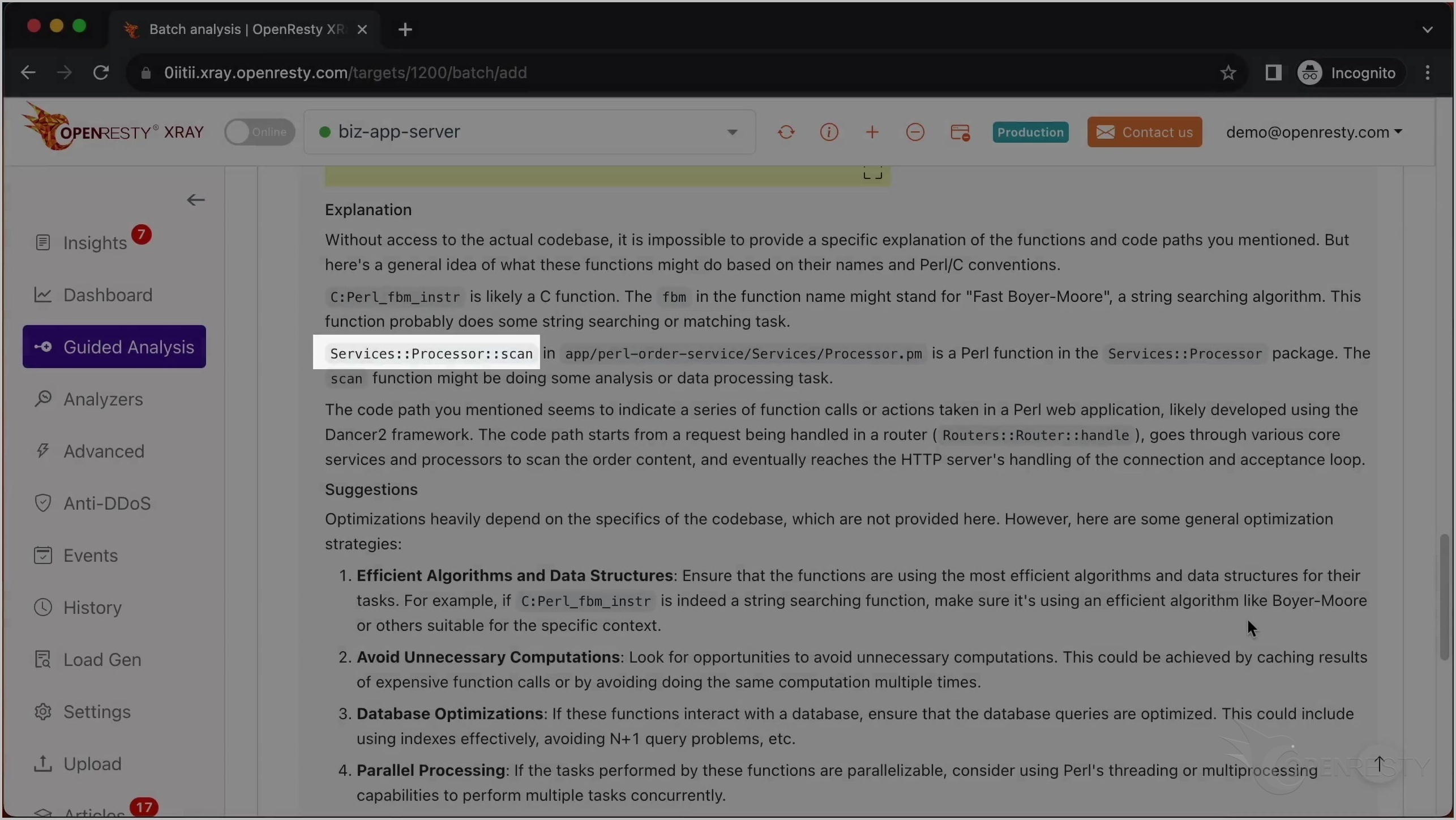
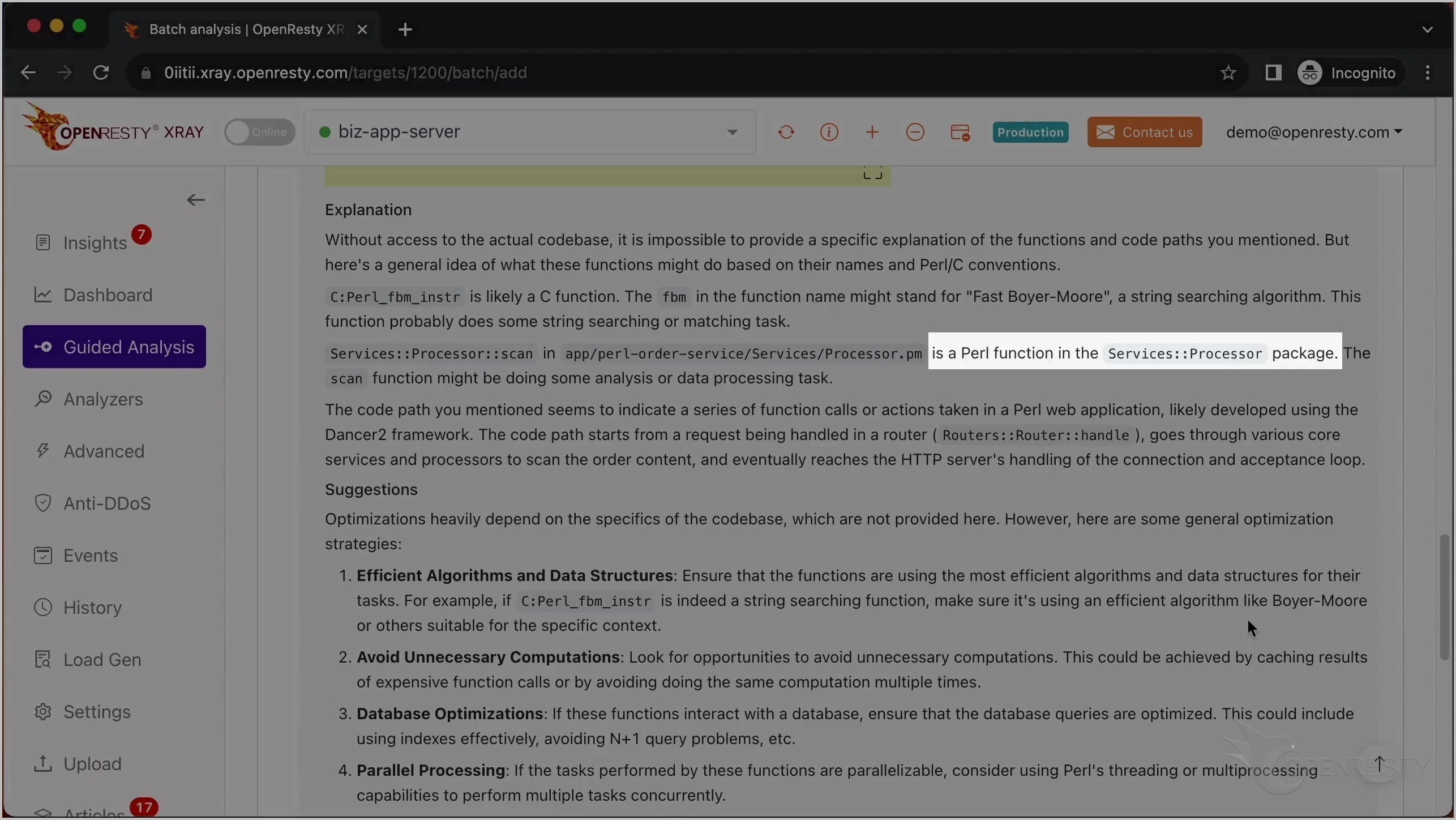
これは scan という名前の Perl 関数です。これはビジネスロジックの一部で、Services::Processor パッケージ内にあります。
呼び出し元であるこれら 2 つの Perl 関数は、ビジネスコードレベルでより多くのコンテキスト情報を提供しています。
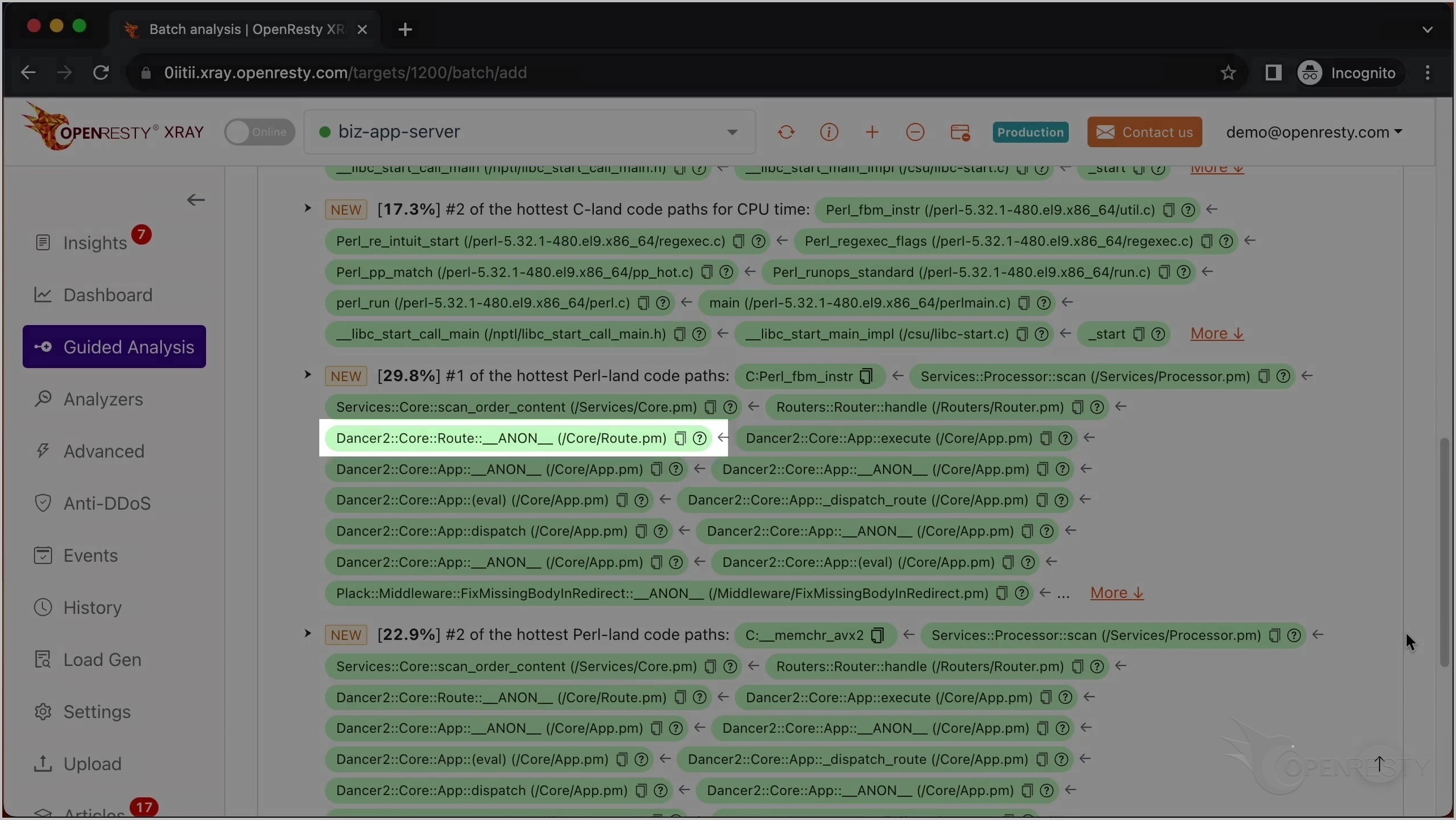
この Perl 関数は Dancer2 Perl Web フレームワークに属しています。
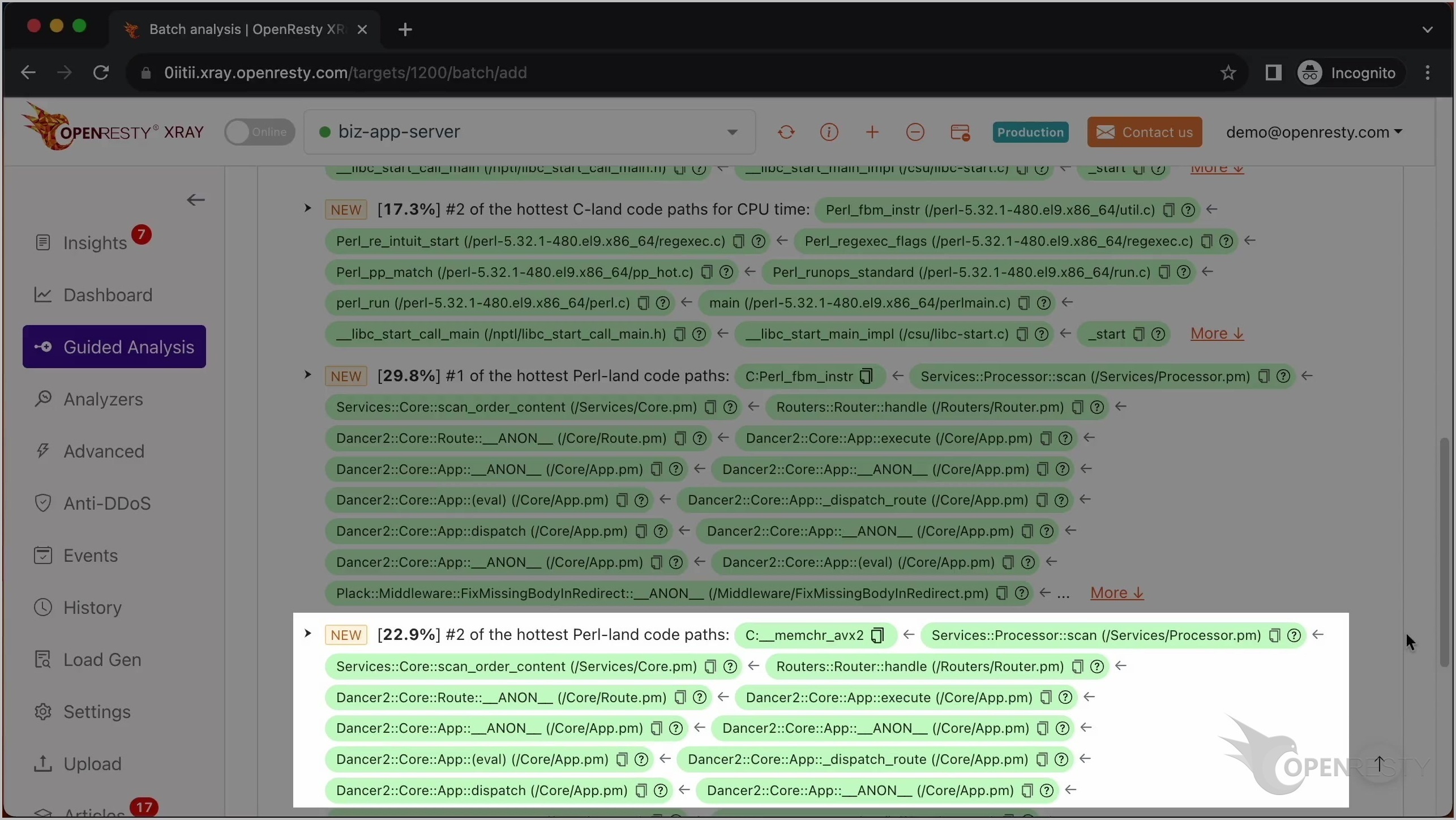
これは 2 番目に CPU 使用率の高い Perl コードパスです。
唯一の違いは、この Glibc 関数 memchr です。これは Intel AVX2 命令セットを使用してメモリバッファ内の文字を検索しています。これも正規表現マッチング操作の一部です。Perl 関数の呼び出しチェーンは全く同じです。
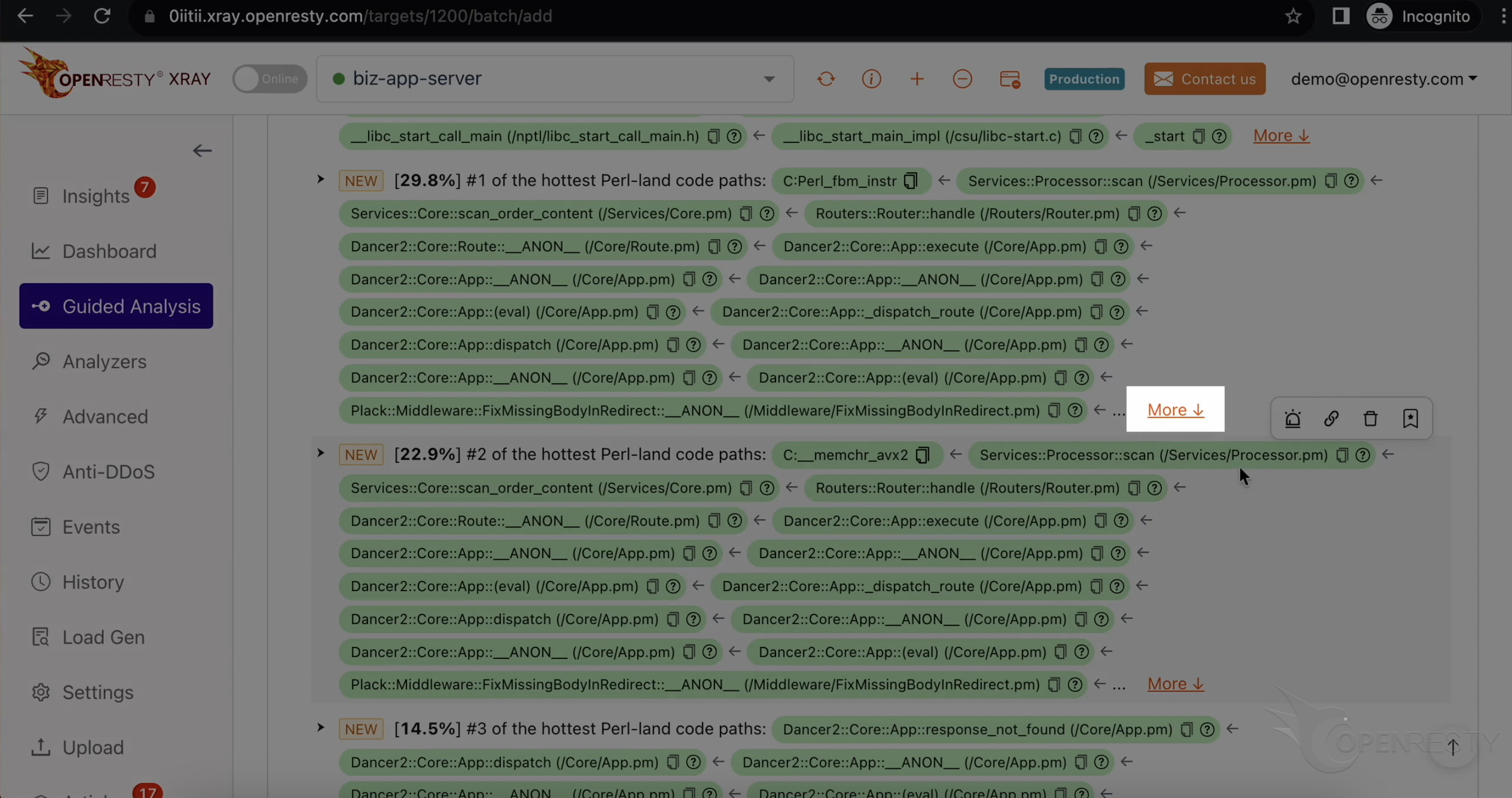
「More」をクリックして、最も CPU 使用率の高い Perl コードパスに関する詳細情報を確認します。
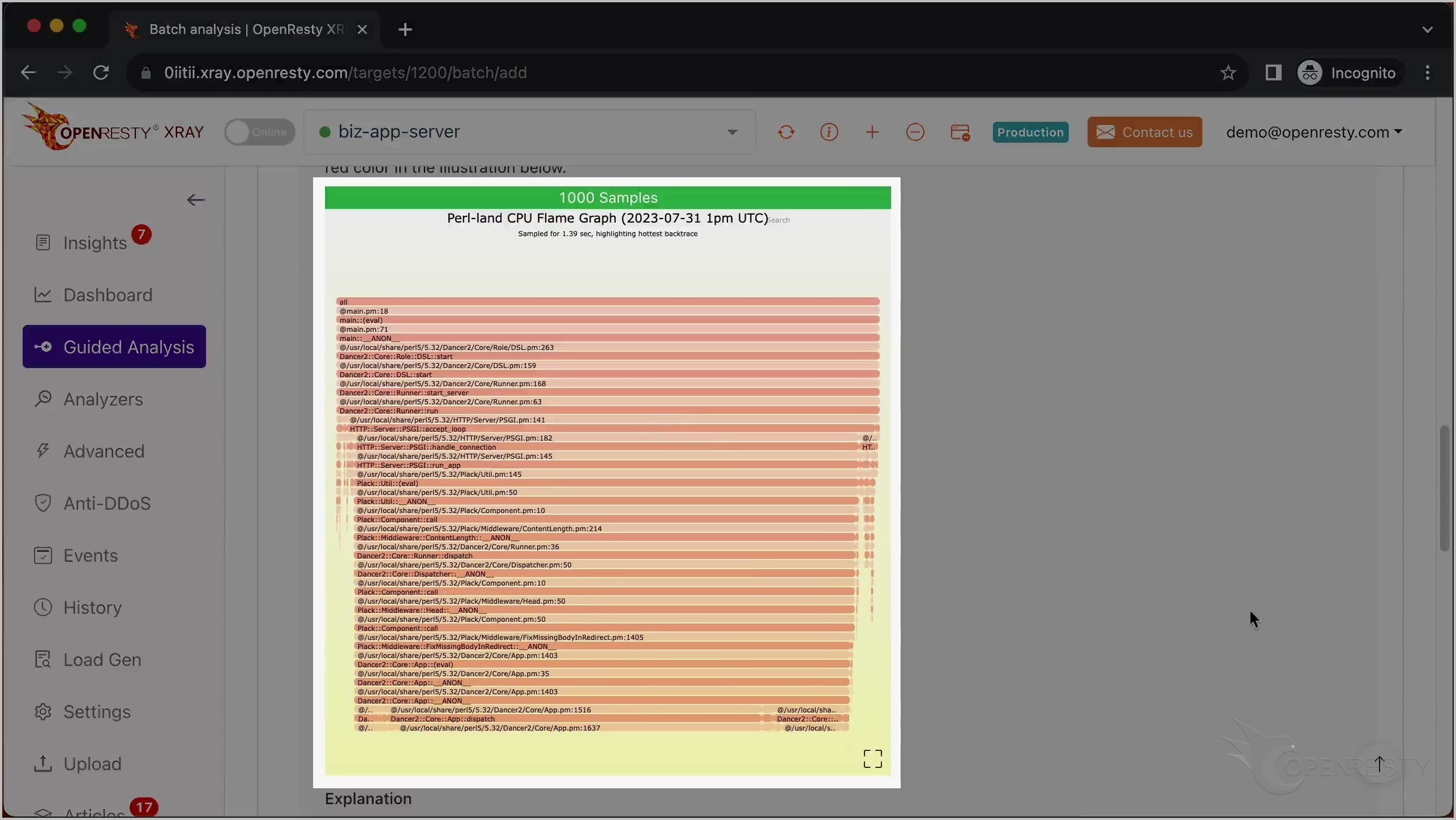
上記に示されたコードパスは、この Perl 言語レベルの CPU フレームグラフから自動的に導き出されたものです。
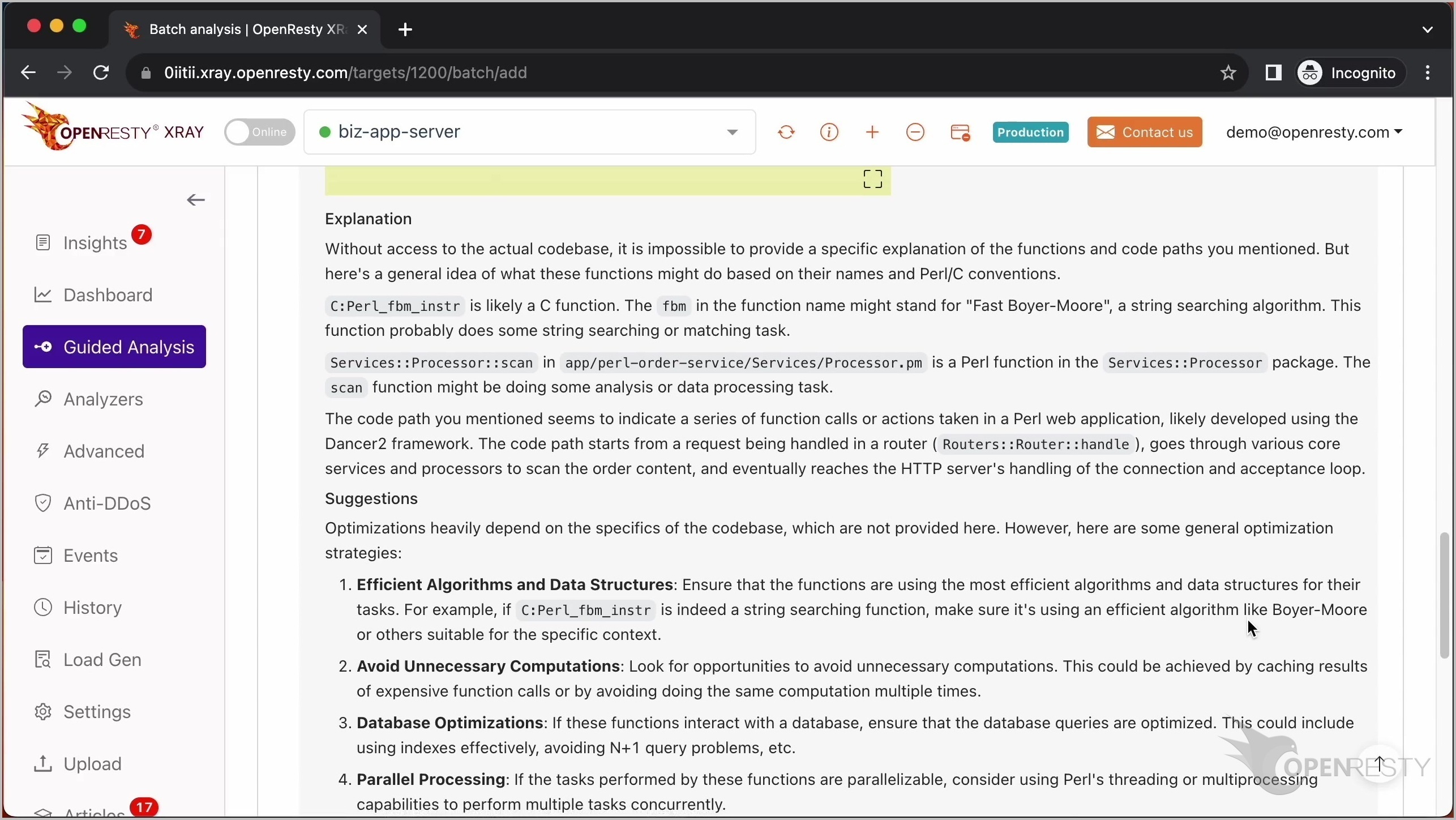
以下は、現在の問題についてのより詳細な説明と提案です。
これは先ほど見た Perl_fbm_instr C 関数について言及しています。
この関数が Fast Boyer-Moore 文字列検索アルゴリズムを使用していることに触れています。
また、Perl 関数 scan についても言及しています。
この関数が Services:Processor パッケージ内にあることを指摘しています。
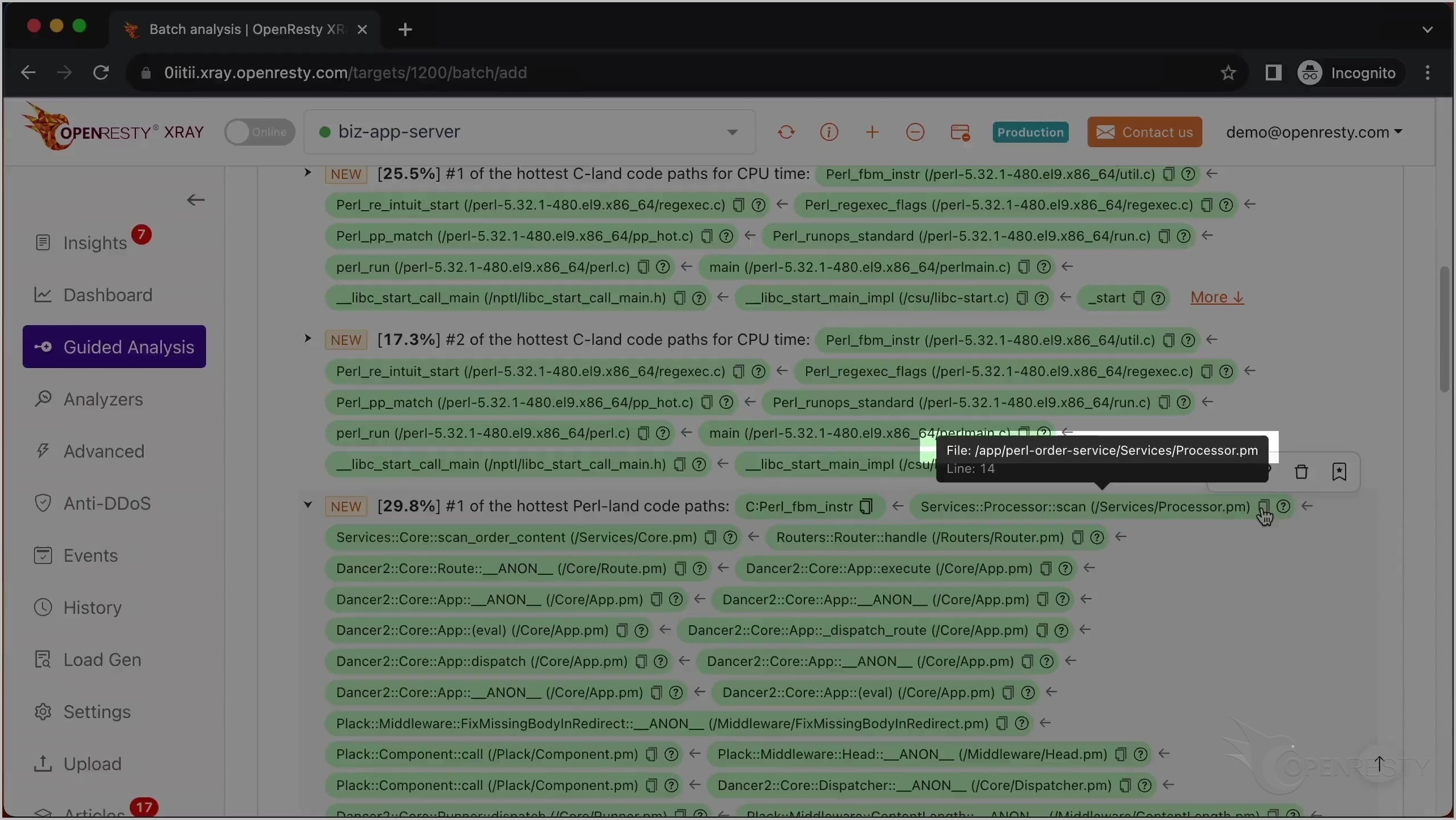
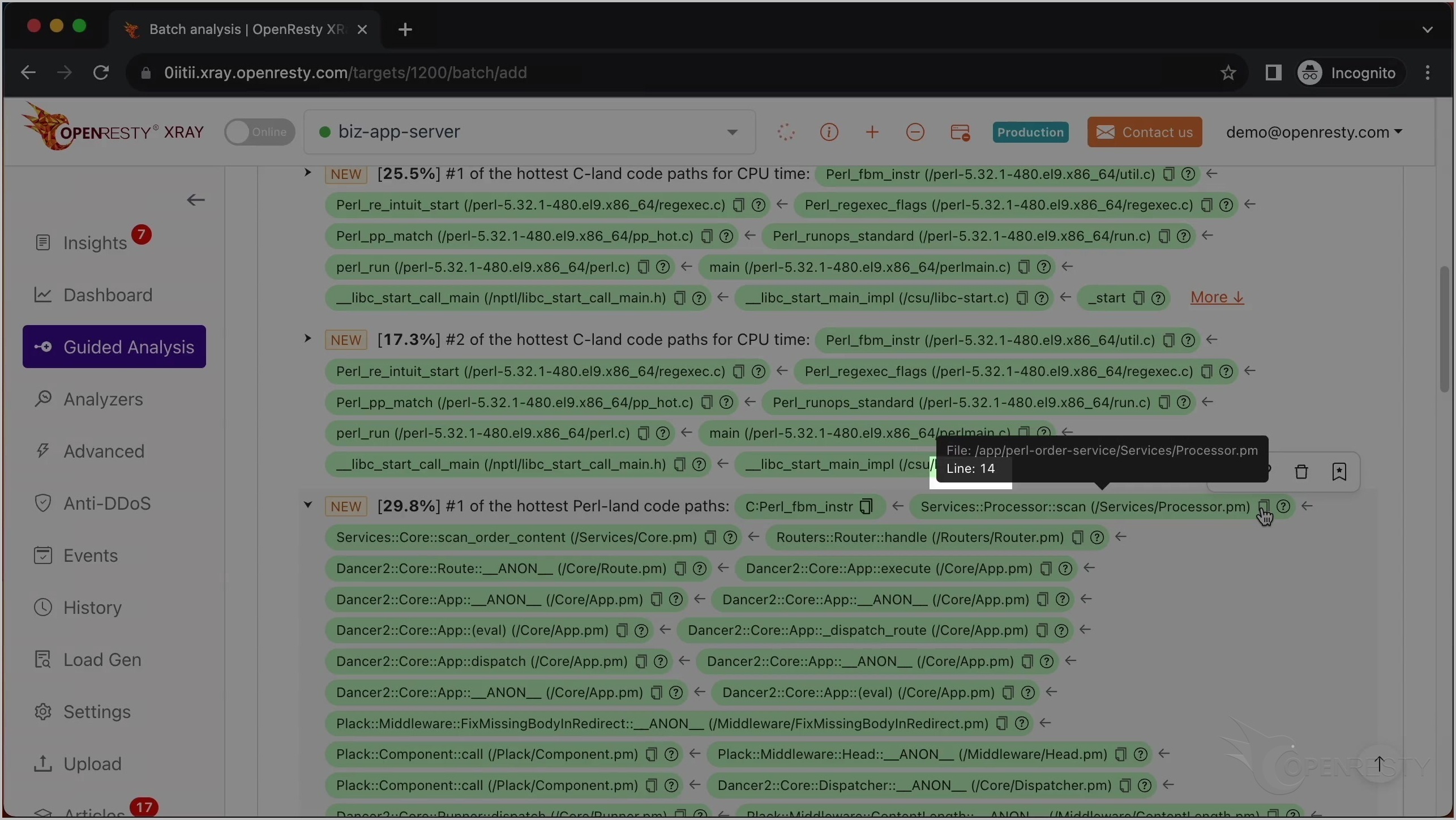
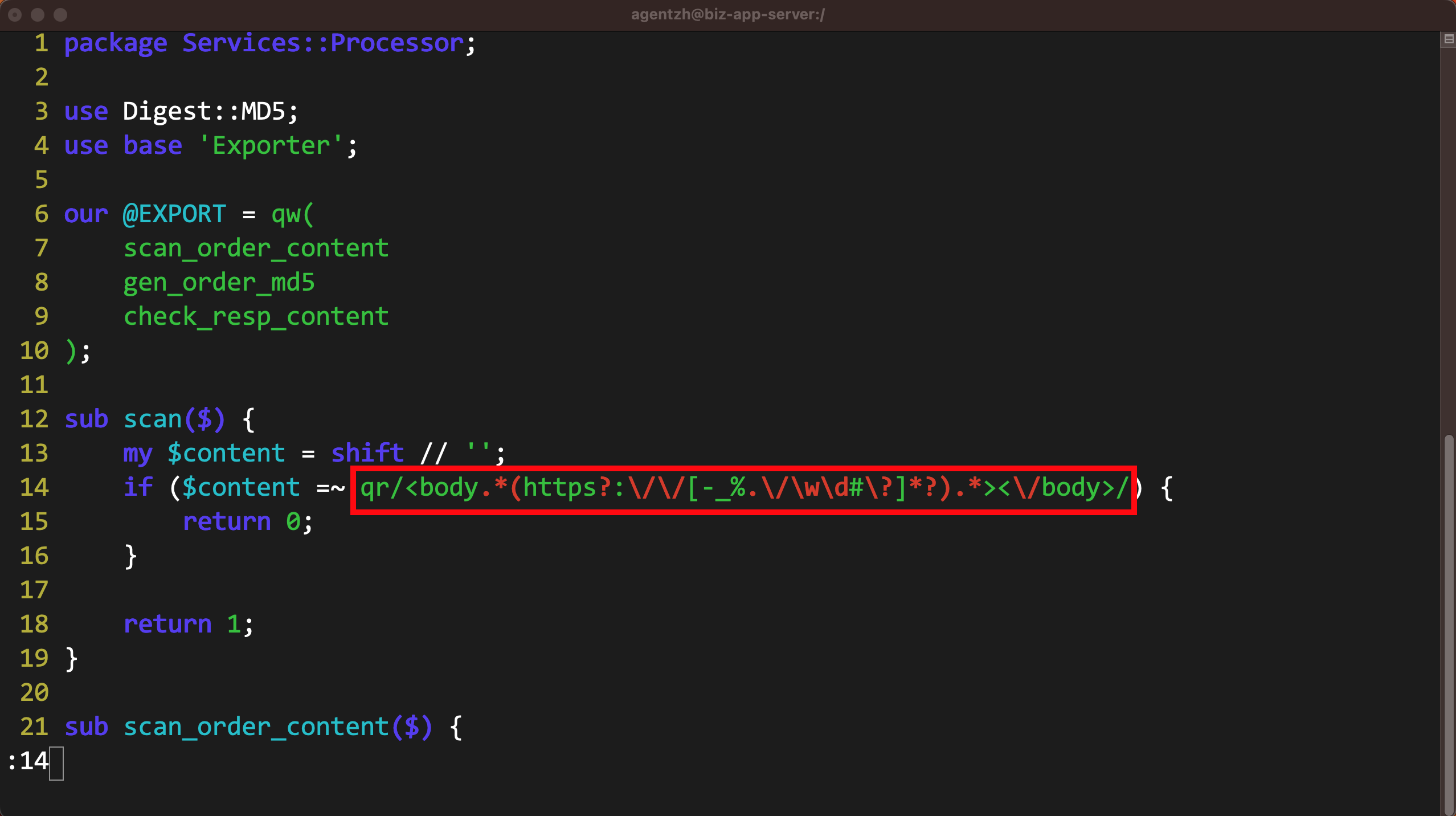
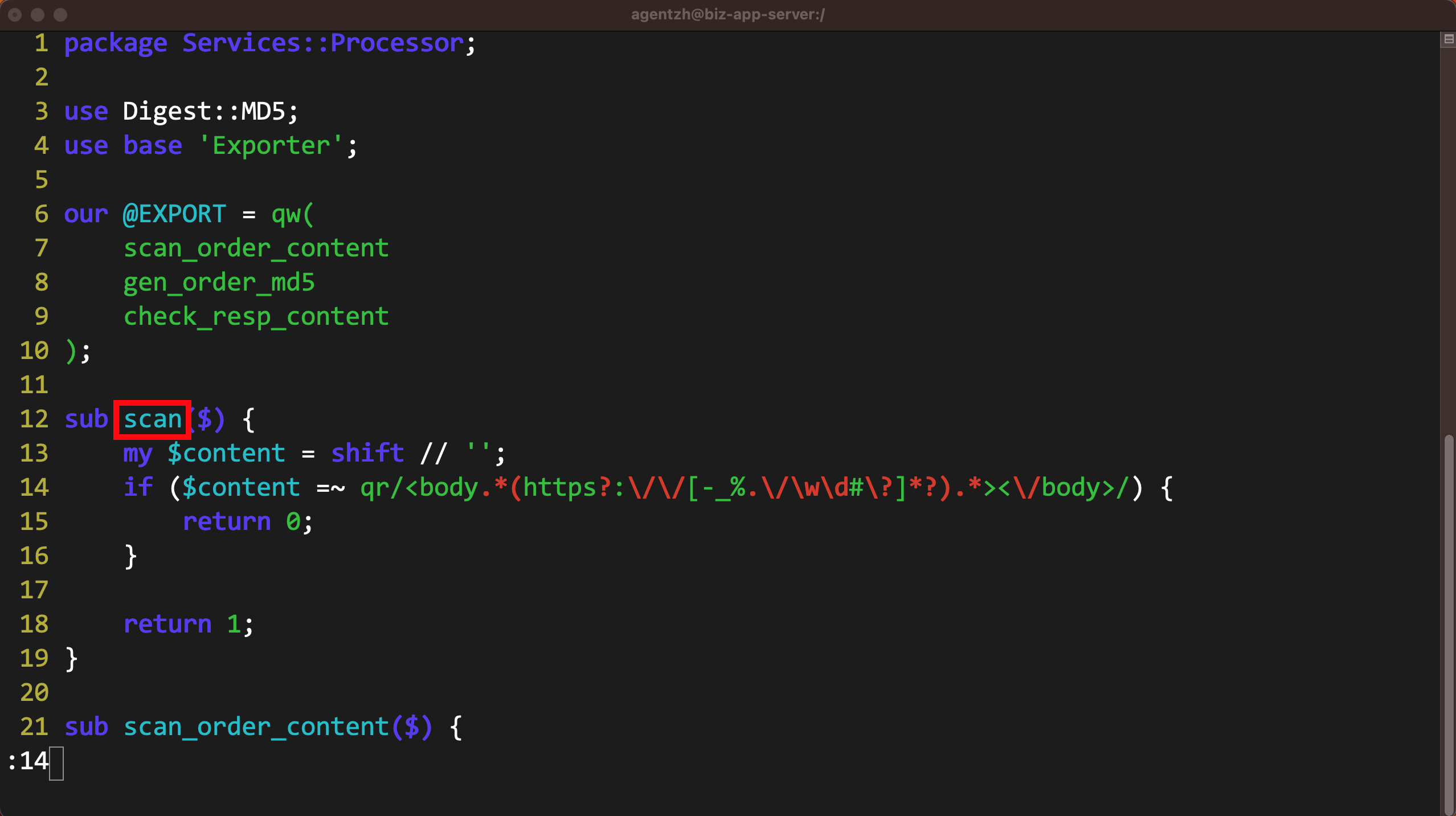
scan という名前の Perl 関数の緑色のボックスにマウスを合わせてください。
scan 関数の Perl ソースファイルが見えます。また、ツールチップに Processor.pm ファイルの完全なパスが表示されています。
Perl ソースコードの行番号は 14 です。
この小さなアイコンをクリックして、関数の完全な Perl ソースファイルパスをコピーします。
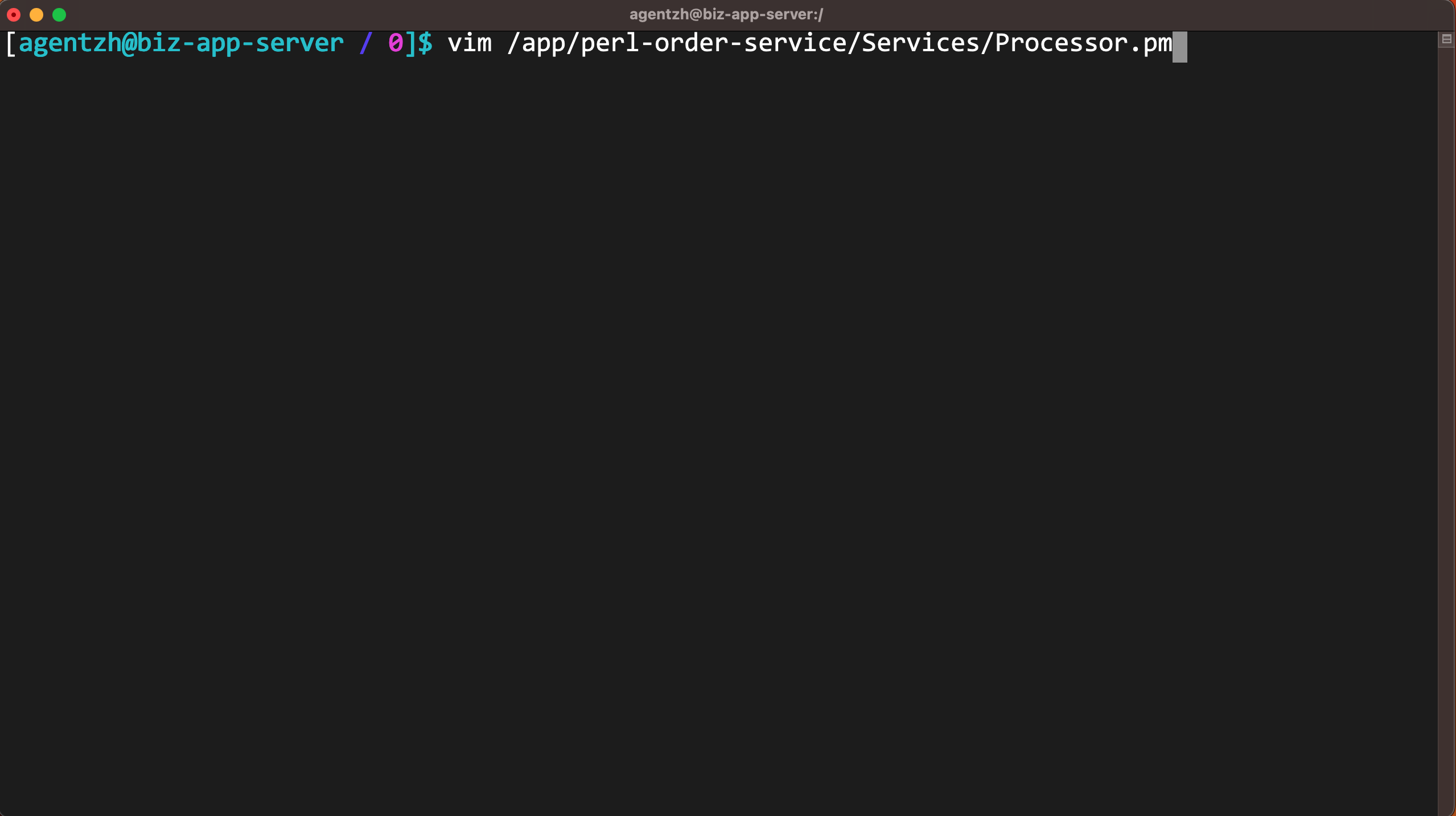
ターミナルで、先ほどコピーしたコードパスを貼り付け、vim エディタを使用して対応する Perl ビジネスコードを確認します。お好みの他のエディタを使用しても構いません。
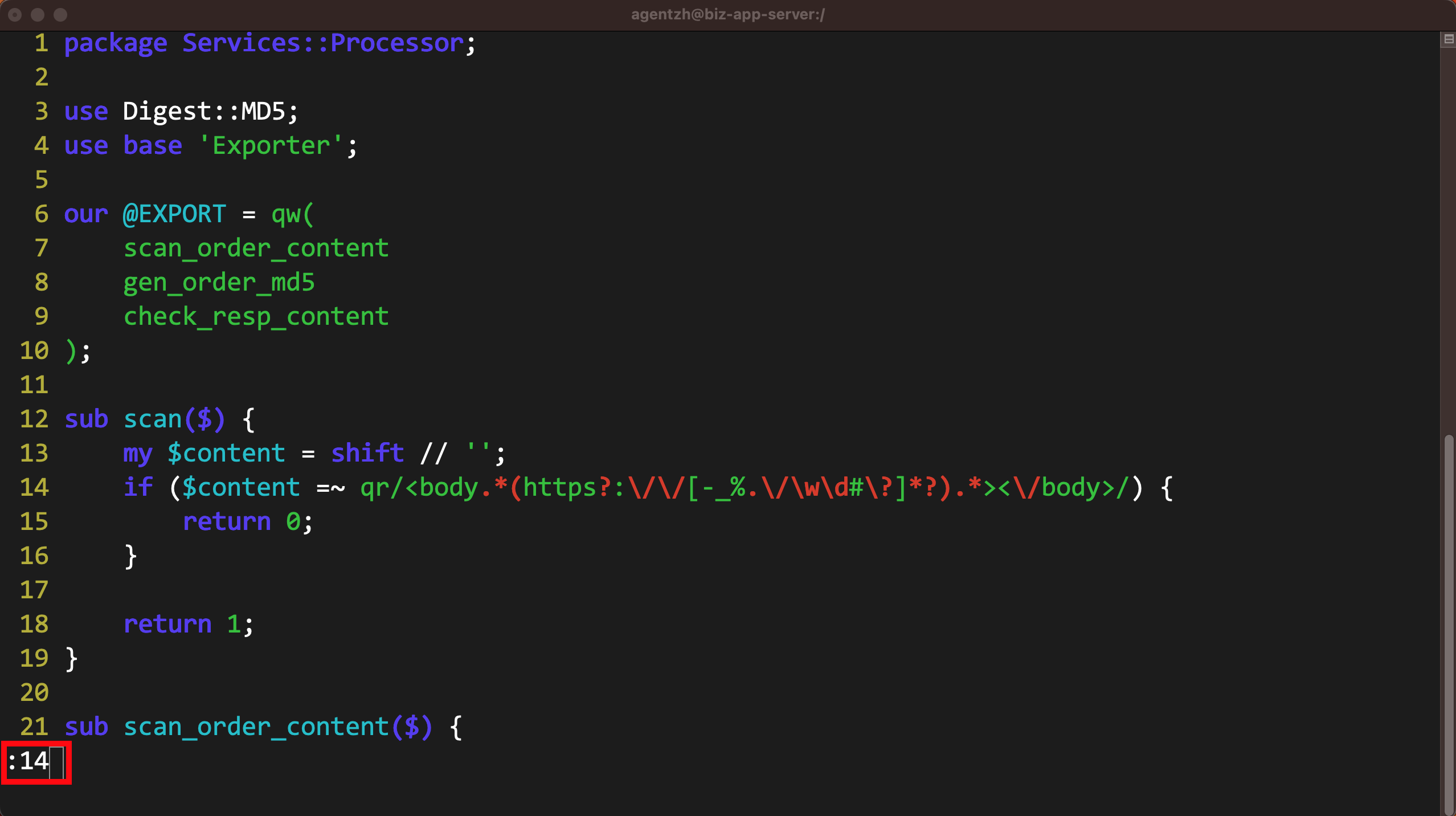
レポートのツールチップに表示されていた 14 行目にジャンプします。
この Perl コード行が確かに正規表現マッチングを行っていることがわかります。
これはレポートに表示されていた scan 関数内にあります。
自動生成レポート
OpenResty XRay はオンラインプロセスを自動的に監視し、分析レポートを生成することができます。
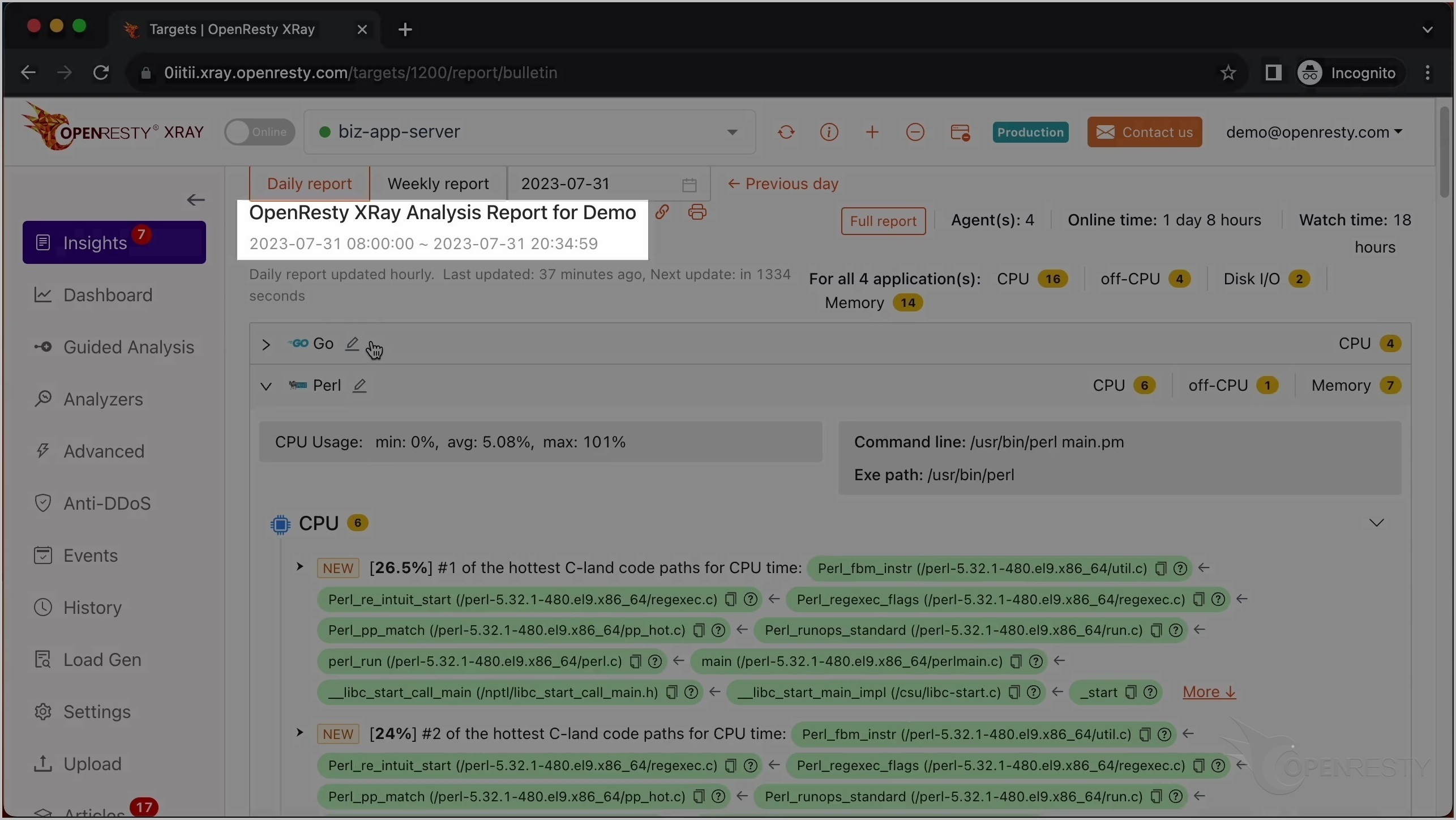
「Insights」ページに切り替えてください。
「Insights」ページでは、日次および週次のレポートを確認することができます。
したがって、「Guided Analysis」機能を必ずしも使用する必要はありません。もちろん、「Guided Analysis」はアプリケーションの開発やデモンストレーションに非常に有用です。
OpenResty XRay について
OpenResty XRay は動的トレーシング製品であり、実行中のアプリケーションを自動的に分析して、パフォーマンスの問題、動作の問題、セキュリティの脆弱性を解決し、実行可能な提案を提供いたします。基盤となる実装において、OpenResty XRay は弊社の Y 言語によって駆動され、Stap+、eBPF+、GDB、ODB など、様々な環境下で複数の異なるランタイムをサポートしております。
著者について
章亦春(Zhang Yichun)は、オープンソースの OpenResty® プロジェクトの創始者であり、OpenResty Inc. の CEO および創業者です。
章亦春(GitHub ID: agentzh)は中国江蘇省生まれで、現在は米国ベイエリアに在住しております。彼は中国における初期のオープンソース技術と文化の提唱者およびリーダーの一人であり、Cloudflare、Yahoo!、Alibaba など、国際的に有名なハイテク企業に勤務した経験があります。「エッジコンピューティング」、「動的トレーシング」、「機械プログラミング」 の先駆者であり、22 年以上のプログラミング経験と 16 年以上のオープンソース経験を持っております。世界中で 4000 万以上のドメイン名を持つユーザーを抱えるオープンソースプロジェクトのリーダーとして、彼は OpenResty® オープンソースプロジェクトをベースに、米国シリコンバレーの中心部にハイテク企業 OpenResty Inc. を設立いたしました。同社の主力製品である OpenResty XRay動的トレーシング技術を利用した非侵襲的な障害分析および排除ツール)と OpenResty XRay(マイクロサービスおよび分散トラフィックに最適化された多機能
翻訳
英語版の原文と日本語訳版(本文)をご用意しております。読者の皆様による他の言語への翻訳版も歓迎いたします。全文翻訳で省略がなければ、採用を検討させていただきます。心より感謝申し上げます!